diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index c3e235a..b9951b7 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -134,16 +134,19 @@
### 🍅链表篇
-- [【动画模拟】剑指 offer 2 倒数第 k 个节点](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/%E5%89%91%E6%8C%87offer2%E5%80%92%E6%95%B0%E7%AC%ACk%E4%B8%AA%E8%8A%82%E7%82%B9.md)
+- [【动画模拟】剑指 offer 22 倒数第 k 个节点](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/%E5%89%91%E6%8C%87offer22%E5%80%92%E6%95%B0%E7%AC%ACk%E4%B8%AA%E8%8A%82%E7%82%B9.md)
- [【动画模拟】面试题 02.03. 链表中间节点](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/%E9%9D%A2%E8%AF%95%E9%A2%98%2002.03.%20%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E4%B8%AD%E9%97%B4%E8%8A%82%E7%82%B9.md)
-- [【动画模拟】剑指 offer 52 两个链表的第一个公共节点](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/%E5%89%91%E6%8C%87Offer52%E4%B8%A4%E4%B8%AA%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%9A%84%E7%AC%AC%E4%B8%80%E4%B8%AA%E5%85%AC%E5%85%B1%E8%8A%82%E7%82%B9.md)
+- [【动画模拟】剑指 offer 52 两个链表的第一个公共节点 & leetcode 160 相交链表](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/%E5%89%91%E6%8C%87Offer52%E4%B8%A4%E4%B8%AA%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%9A%84%E7%AC%AC%E4%B8%80%E4%B8%AA%E5%85%AC%E5%85%B1%E8%8A%82%E7%82%B9.md)
- [【动画模拟】leetcode 234 回文链表](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/234.%20%E5%9B%9E%E6%96%87%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8.md)
- [【动画模拟】leetcode 206 反转链表](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/leetcode206%E5%8F%8D%E8%BD%AC%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8.md)
-- [【动画模拟】leetcode92反转链表2](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/leetcode92%E5%8F%8D%E8%BD%AC%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A82.md)
+- [【动画模拟】leetcode 92 反转链表2](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/leetcode92%E5%8F%8D%E8%BD%AC%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A82.md)
+- [【动画模拟】leetcode 141 环形链表](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/leetcode141%E7%8E%AF%E5%BD%A2%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8.md)
- [【动画模拟】leetcode 142 环形链表2](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/leetcode142%E7%8E%AF%E5%BD%A2%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A82.md)
- [【动画模拟】leetcode 86 分隔链表](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/leetcode86%E5%88%86%E9%9A%94%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8.md)
+- [【动画模拟】leetcode 328 奇偶链表](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/leetcode328%E5%A5%87%E5%81%B6%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8.md)
- [【动画模拟】剑指 offer 25 合并两个排序链表](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/%E5%89%91%E6%8C%87Offer25%E5%90%88%E5%B9%B6%E4%B8%A4%E4%B8%AA%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E7%9A%84%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8.md)
- [【动画模拟】leetcode 82 删除排序链表的重复元素2](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/leetcode82%E5%88%A0%E9%99%A4%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84%E9%87%8D%E5%A4%8D%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0II.md)
+- [【动画模拟】leetcode 147 对链表进行插入排序](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/leetcode147%E5%AF%B9%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E8%BF%9B%E8%A1%8C%E6%8F%92%E5%85%A5%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F.md)
- [【动画模拟】面试题 02.05 链表求和](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/%E9%9D%A2%E8%AF%95%E9%A2%98%2002.05.%20%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E6%B1%82%E5%92%8C.md)
### 🚁双指针
@@ -214,7 +217,7 @@
### 🌋并查集
-
+- 敬请期待。。。
------
@@ -270,4 +273,3 @@

-###### ####
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/234. 回文链表.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/234. 回文链表.md
index fe3e1ed..cee4772 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/234. 回文链表.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/234. 回文链表.md
@@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
-
-
> 如果阅读时,发现错误,或者动画不可以显示的问题可以添加我微信好友 **[tan45du_one](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/tan45du.github.io/master/个人微信.15egrcgqd94w.jpg)** ,备注 github + 题目 + 问题 向我反馈
>
> 感谢支持,该仓库会一直维护,希望对各位有一丢丢帮助。
@@ -35,6 +33,8 @@
**题目代码**
+Java Code:
+
```java
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ class Solution {
arr.add(copynode.val);
copynode = copynode.next;
}
- // 双指针遍历数组
+ //双指针遍历数组
int back = 0;
int pro = arr.size() - 1;
while (back < pro) {
@@ -61,12 +61,93 @@ class Solution {
return true;
}
}
+```
+C++ Code:
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
+ //这里需要用动态数组,因为我们不知道链表的长度
+ vector arr;
+ ListNode* copynode = head;
+ //将链表的值复制到数组中
+ while (copynode) {
+ arr.push_back(copynode->val);
+ copynode = copynode->next;
+ }
+ //双指针遍历数组
+ int back = 0;
+ int pro = arr.size() - 1;
+ while (back < pro) {
+ //判断两个指针的值是否相等
+ if (arr[back] != arr[pro]) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ //移动指针
+ back++;
+ pro--;
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+JS Code:
+
+```js
+var isPalindrome = function(head) {
+ let arr = [];
+ let copynode = head;
+ //将链表的值复制到数组中
+ while (copynode) {
+ arr.push(copynode.val)
+ copynode = copynode.next
+ }
+ //双指针遍历数组
+ let back = 0;
+ let pro = arr.length - 1;
+ while (back < pro) {
+ //判断两个指针的值是否相等
+ if (arr[back] !== arr[pro]) {
+ return false
+ }
+ //移动指针
+ back += 1
+ pro -= 1
+ }
+ return true
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
+ arr = []
+ copynode = head
+ # 将链表的值复制到数组中
+ while copynode is not None:
+ arr.append(copynode.val)
+ copynode = copynode.next
+ # 双指针遍历数组
+ back = 0
+ pro = len(arr) - 1
+ while back < pro:
+ # 判断两个指针的值是否相等
+ if arr[back] != arr[pro]:
+ return False
+ # 移动指针
+ back += 1
+ pro -= 1
+ return True
```
这个方法可以直接通过,但是这个方法需要辅助数组,那我们还有其他更好的方法吗?
-双指针翻转链表法
+**双指针翻转链表法**
在上个题目中我们知道了如何找到链表的中间节点,那我们可以在找到中间节点之后,对后半部分进行翻转,翻转之后,重新遍历前半部分和后半部分进行判断是否为回文。
@@ -82,37 +163,35 @@ Java Code:
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head==null || head.next==null) {
- return true;
+ return true;
}
//找到中间节点,也就是翻转的头节点,这个在昨天的题目中讲到
//但是今天和昨天有一些不一样的地方就是,如果有两个中间节点返回第一个,昨天的题目是第二个
- ListNode midenode = searchmidnode(head);
+ ListNode midnode = searchmidnode(head);
//原地翻转链表,需要两个辅助指针。这个也是面试题目,大家可以做一下
//这里我们用的是midnode.next需要注意,因为我们找到的是中点,但是我们翻转的是后半部分
-
- ListNode backhalf = reverse(midenode.next);
+ ListNode backhalf = reverse(midnode.next);
//遍历两部分链表,判断值是否相等
ListNode p1 = head;
ListNode p2 = backhalf;
while (p2 != null) {
if (p1.val != p2.val) {
- return false;
+ //若要还原,记得这里也要reverse
+ midnode.next = reverse(backhalf);
+ return false;
}
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
- // 还原链表并返回结果,这一步是需要注意的,我们不可以破坏初始结构,我们只是判断是否为回文,
+ //还原链表并返回结果,这一步是需要注意的,我们不可以破坏初始结构,我们只是判断是否为回文,
//当然如果没有这一步也是可以AC,但是面试的时候题目要求可能会有这一条。
- midenode.next = reverse(backhalf);
+ midnode.next = reverse(backhalf);
return true;
}
- //找到中间的部分
- public ListNode searchmidnode (ListNode head) {
- ListNode fast = new ListNode(-1);
- ListNode slow = new ListNode(-1);
- fast = head;
- slow = head;
- //找到中点
+ //找到中点
+ public ListNode searchmidnode (ListNode head) {
+ ListNode fast = head;
+ ListNode slow = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
@@ -123,12 +202,11 @@ class Solution {
public ListNode reverse (ListNode slow) {
ListNode low = null;
ListNode temp = null;
- //翻转链表
while (slow != null) {
- temp = slow.next;
- slow.next = low;
- low = slow;
- slow = temp;
+ temp = slow.next;
+ slow.next = low;
+ low = slow;
+ slow = temp;
}
return low;
}
@@ -144,35 +222,33 @@ public:
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) {
return true;
}
- //找到中间节点,也就是翻转的头节点,这个在昨天的题目中讲到
+ //找到中间节点,也就是翻转的头节点,这个在昨天的题目中讲到
//但是今天和昨天有一些不一样的地方就是,如果有两个中间节点返回第一个,昨天的题目是第二个
- ListNode * midenode = searchmidnode(head);
+ ListNode * midnode = searchmidnode(head);
//原地翻转链表,需要两个辅助指针。这个也是面试题目,大家可以做一下
//这里我们用的是midnode->next需要注意,因为我们找到的是中点,但是我们翻转的是后半部分
-
- ListNode * backhalf = reverse(midenode->next);
+ ListNode * backhalf = reverse(midnode->next);
//遍历两部分链表,判断值是否相等
ListNode * p1 = head;
ListNode * p2 = backhalf;
while (p2 != nullptr) {
if (p1->val != p2->val) {
- return false;
+ //若要还原,记得这里也要reverse
+ midnode->next = reverse(backhalf);
+ return false;
}
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
}
- // 还原链表并返回结果,这一步是需要注意的,我们不可以破坏初始结构,我们只是判断是否为回文,
+ //还原链表并返回结果,这一步是需要注意的,我们不可以破坏初始结构,我们只是判断是否为回文,
//当然如果没有这一步也是可以AC,但是面试的时候题目要求可能会有这一条。
- midenode->next = reverse(backhalf);
+ midnode->next = reverse(backhalf);
return true;
}
//找到中间的部分
- ListNode * searchmidnode (ListNode * head) {
- ListNode * fast = new ListNode(-1);
- ListNode * slow = new ListNode(-1);
- fast = head;
- slow = head;
- //找到中点
+ ListNode * searchmidnode (ListNode * head) {
+ ListNode * fast = head;
+ ListNode * slow = head;
while (fast->next != nullptr && fast->next->next != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
@@ -183,15 +259,119 @@ public:
ListNode * reverse (ListNode * slow) {
ListNode * low = nullptr;
ListNode * temp = nullptr;
- //翻转链表
while (slow != nullptr) {
- temp = slow->next;
- slow->next = low;
- low = slow;
- slow = temp;
+ temp = slow->next;
+ slow->next = low;
+ low = slow;
+ slow = temp;
}
return low;
}
};
```
+JS Code:
+
+```javascript
+var isPalindrome = function(head) {
+ if (head === null || head.next === null) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ //找到中间节点,也就是翻转的头节点,这个在昨天的题目中讲到
+ //但是今天和昨天有一些不一样的地方就是,如果有两个中间节点返回第一个,昨天的题目是第二个
+ let midnode = searchmidnode(head);
+ //原地翻转链表,需要两个辅助指针。这个也是面试题目,大家可以做一下
+ //这里我们用的是midnode.next需要注意,因为我们找到的是中点,但是我们翻转的是后半部分
+ let backhalf = reverse(midnode.next);
+ //遍历两部分链表,判断值是否相等
+ let p1 = head;
+ let p2 = backhalf;
+ while (p2 != null) {
+ if (p1.val != p2.val) {
+ //若要还原,记得这里也要reverse
+ midnode.next = reverse(backhalf);
+ return false;
+ }
+ p1 = p1.next;
+ p2 = p2.next;
+ }
+ //还原链表并返回结果,这一步是需要注意的,我们不可以破坏初始结构,我们只是判断是否为回文,
+ //当然如果没有这一步也是可以AC,但是面试的时候题目要求可能会有这一条。
+ midnode.next = reverse(backhalf);
+ return true;
+};
+
+//找到中点
+var searchmidnode = function(head) {
+ let fast = head;
+ let slow = head;
+ while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
+ fast = fast.next.next;
+ slow = slow.next;
+ }
+ return slow;
+};
+
+//翻转链表
+var reverse = function(slow) {
+ let low = null;
+ let temp = null;
+ while (slow != null) {
+ temp = slow.next;
+ slow.next = low;
+ low = slow;
+ slow = temp;
+ }
+ return low;
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
+ if head is None or head.next is None:
+ return True
+ # 找到中间节点,也就是翻转的头节点,这个在昨天的题目中讲到
+ # 但是今天和昨天有一些不一样的地方就是,如果有两个中间节点返回第一个,昨天的题目是第二个
+ midnode = self.searchmidnode(head)
+ # 原地翻转链表,需要两个辅助指针。这个也是面试题目,大家可以做一下
+ # 这里我们用的是midnode.next需要注意,因为我们找到的是中点,但是我们翻转的是后半部分
+ backhalf = self.reverse(midnode.next)
+ # 遍历两部分链表,判断值是否相等
+ p1 = head
+ p2 = backhalf
+ while p2 is not None:
+ if p1.val != p2.val:
+ # 若要还原,记得这里也要reverse
+ midnode.next = self.reverse(backhalf)
+ return False
+ p1 = p1.next
+ p2 = p2.next
+ # 还原链表并返回结果,这一步是需要注意的,我们不可以破坏初始结构,我们只是判断是否为回文,
+ # 当然如果没有这一步也是可以AC,但是面试的时候题目要求可能会有这一条。
+ midnode.next = self.reverse(backhalf)
+ return True
+
+ # 找到中点
+ def searchmidnode(self, head):
+ fast = head
+ slow = head
+ while fast.next is not None and fast.next.next is not None:
+ fast = fast.next.next
+ slow = slow.next
+ return slow
+
+ # 翻转链表
+ def reverse(self, slow):
+ low = None
+ temp = None
+ while slow is not None:
+ temp = slow.next
+ slow.next = low
+ low = slow
+ slow = temp
+ return low
+```
+
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode141环形链表.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode141环形链表.md
index 2992b60..b0e186f 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode141环形链表.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode141环形链表.md
@@ -10,9 +10,9 @@
#### 题目描述
-> 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。pos代表环的入口,若为-1,则代表无环
+> 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。pos代表环的入口,若为-1,则代表无环。
>
-> 如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
+> 如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。否则,返回 false 。
示例1:
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@

-好啦,做题思路已经有了,让我们一起看一下代码的执行过程吧。\
+好啦,做题思路已经有了,让我们一起看一下代码的执行过程吧。
**动画模拟**
@@ -42,7 +42,6 @@ Java Code:
```java
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
-
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode low = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
@@ -57,7 +56,28 @@ public class Solution {
}
```
+C++ Code:
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
+ ListNode * fast = head;
+ ListNode * slow = head;
+ while (fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) {
+ fast = fast->next->next;
+ slow = slow->next;
+ if (fast == slow) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+};
+```
+
JS Code:
+
```javascript
var hasCycle = function(head) {
let fast = head;
@@ -73,23 +93,18 @@ var hasCycle = function(head) {
};
```
-C++ Code:
+Python Code:
-```cpp
-class Solution {
-public:
- bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
- ListNode * fast = head;
- ListNode * low = head;
- while (fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) {
- fast = fast->next->next;
- low = low->next;
- if (fast == low) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
-};
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
+ fast = head
+ slow = head
+ while fast and fast.next:
+ fast = fast.next.next
+ slow = slow.next
+ if fast == slow:
+ return True
+ return False
```
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode142环形链表2.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode142环形链表2.md
index 29ed3da..e942a74 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode142环形链表2.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode142环形链表2.md
@@ -18,33 +18,7 @@
我们可以这样假设,两个孩子在操场顺时针跑步,一个跑的快,一个跑的慢,跑的快的那个孩子总会追上跑的慢的孩子。
-环形链表:
-
-```java
-public class Solution {
- public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
- //特殊情况,无节点或只有一个节点的情况
- if(head == null || head.next == null){
- return false;
- }
- //设置快慢指针
- ListNode pro = head.next;
- ListNode last = head;
- //循环条件
- while( pro != null && pro.next!=null){
- pro=pro.next.next;
- last=last.next;
- //两指针相遇
- if(pro == last){
- return true;
- }
- }
- //循环结束,指针没有相遇,说明没有环。相当于快指针遍历了一遍链表
- return false;
-
- }
-}
-```
+代码请参考[【动画模拟】leetcode 141 环形链表](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/leetcode141%E7%8E%AF%E5%BD%A2%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8.md)。
判断链表是不是含有环很简单,但是我们想找到环的入口可能就没有那么容易了。(入口则为下图绿色节点)
@@ -62,23 +36,22 @@ public class Solution {

-
+Java Code:
```java
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
-
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
if (head.next == null) {
return head.next;
}
- //创建新的HashSet,用于保存节点
+ //创建新的HashSet,用于保存节点
HashSet hash = new HashSet();
//遍历链表
while (head != null) {
- //判断哈希表中是否含有某节点,没有则保存,含有则返回该节点
+ //判断哈希表中是否含有某节点,没有则保存,含有则返回该节点
if (hash.contains(head)) {
return head;
}
@@ -91,6 +64,74 @@ public class Solution {
}
```
+C++ Code:
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
+ if (head == nullptr) return head;
+ if (head->next == nullptr) return head->next;
+ //创建新的HashSet,用于保存节点
+ set hash;
+ //遍历链表
+ while (head != nullptr) {
+ //判断哈希表中是否含有某节点,没有则保存,含有则返回该节点
+ if (hash.count(head)) {
+ return head;
+ }
+ //不含有,则进行保存,并移动指针
+ hash.insert(head);
+ head = head->next;
+ }
+ return head;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+JS Code:
+
+```javascript
+var detectCycle = function(head) {
+ if (head === null) return head;
+ if (head.next === null) return head.next;
+ //创建新的HashSet,用于保存节点
+ let hash = new Set();
+ //遍历链表
+ while (head !== null) {
+ //判断哈希表中是否含有某节点,没有则保存,含有则返回该节点
+ if (hash.has(head)) {
+ return head;
+ }
+ //不含有,则进行保存,并移动指针
+ hash.add(head);
+ head = head.next;
+ }
+ return head;
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def detectCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
+ if head is None:
+ return head
+ if head.next is None:
+ return head.next
+ # 创建新的HashSet,用于保存节点
+ hash = set()
+ while head is not None:
+ # 判断哈希表中是否含有某节点,没有则保存,含有则返回该节点
+ if head in hash:
+ return head
+ # 不含有,则进行保存,并移动指针
+ hash.add(head)
+ head = head.next
+ return head
+```
+
### 快慢指针
@@ -101,25 +142,25 @@ public class Solution {
上图黄色节点为快慢指针相遇的节点,此时
-快指针走的距离:**a+(b+c)n+b**
+快指针走的距离:**a+(b+c)n+b**,n代表圈数。
很容易理解b+c为环的长度,a为直线距离,b为绕了n圈之后又走了一段距离才相遇,所以相遇时走的总路程为a+(b+c)n+b,合并同类项得a+(n+1)b+nc。
-慢指针走的距离:**a+(b+c)m+b**,m代表圈数。
+慢指针走的距离:**a+(b+c)m+b**,m代表圈数。
-然后我们设快指针得速度是慢指针的2倍,含义为相同时间内,快指针走过的距离是慢指针的2倍。
+然后我们设快指针得速度是慢指针的2倍,含义为相同时间内,快指针走过的距离是慢指针的2倍。
-**a+(n+1)b+nc=2[a+(m+1)b+mc]**整理得**a+b=(n-2m)(b+c),**那么我们可以从这个等式上面发现什么呢?**b+c**
+**a+(n+1)b+nc=2[a+(m+1)b+mc]**整理得**a+b=(n-2m)(b+c),**那么我们可以从这个等式上面发现什么呢?
-为一圈的长度。也就是说a+b等于n-2m个环的长度。为了便于理解我们看一种特殊情况,当n-2m等于1,那么a+b=b+c整理得,a=c此时我们只需重新释放两个指针,一个从head释放,一个从相遇点释放,速度相同,因为a=c所以他俩必会在环入口处相遇,则求得入口节点索引。
+**b+c**为一圈的长度。也就是说a+b等于n-2m个环的长度。为了便于理解我们看一种特殊情况,当n-2m等于1,那么a+b=b+c整理得,a=c。此时我们只需重新释放两个指针,一个从head释放,一个从相遇点释放,速度相同,因为a=c所以他俩必会在环入口处相遇,则求得入口节点索引。
算法流程:
-1.设置快慢指针,快指针速度为慢指针的2倍
+1.设置快慢指针,快指针速度为慢指针的2倍。
-2.找出相遇点
+2.找出相遇点。
-3.在head处和相遇点同时释放相同速度且速度为1的指针,两指针必会在环入口处相遇
+3.在head处和相遇点同时释放相同速度且速度为1的指针,两指针必会在环入口处相遇。

@@ -132,25 +173,24 @@ public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
//快慢指针
ListNode fast = head;
- ListNode low = head;
+ ListNode slow = head;
//设置循环条件
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
- low = low.next;
+ slow = slow.next;
//相遇
- if (fast == low) {
+ if (fast == slow) {
//设置一个新的指针,从头节点出发,慢指针速度为1,所以可以使用慢指针从相遇点出发
- ListNode newnode = head;
- while (newnode != low) {
- low = low.next;
- newnode = newnode.next;
+ ListNode newptr = head;
+ while (newptr != slow) {
+ slow = slow.next;
+ newptr = newptr.next;
}
//在环入口相遇
- return low;
+ return slow;
}
}
return null;
-
}
}
```
@@ -163,26 +203,75 @@ public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
//快慢指针
ListNode * fast = head;
- ListNode * low = head;
+ ListNode * slow = head;
//设置循环条件
while (fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next->next;
- low = low->next;
+ slow = slow->next;
//相遇
- if (fast == low) {
+ if (fast == slow) {
//设置一个新的指针,从头节点出发,慢指针速度为1,所以可以使用慢指针从相遇点出发
ListNode * newnode = head;
- while (newnode != low) {
- low = low->next;
+ while (newnode != slow) {
+ slow = slow->next;
newnode = newnode->next;
}
//在环入口相遇
- return low;
+ return slow;
}
}
return nullptr;
-
}
};
```
+JS Code:
+
+```js
+var detectCycle = function(head) {
+ //快慢指针
+ let fast = head;
+ let slow = head;
+ //设置循环条件
+ while (fast && fast.next) {
+ fast = fast.next.next;
+ slow = slow.next;
+ //相遇
+ if (fast == slow) {
+ let newptr = head;
+ //设置一个新的指针,从头节点出发,慢指针速度为1,所以可以使用慢指针从相遇点出发
+ while (newptr != slow) {
+ slow = slow.next;
+ newptr = newptr.next;
+ }
+ //在环入口相遇
+ return slow;
+ }
+ }
+ return null;
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def detectCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
+ # 快慢指针
+ fast = head
+ slow = head
+ # 设置循环条件
+ while fast is not None and fast.next is not None:
+ fast = fast.next.next
+ slow = slow.next
+ # 相遇
+ if fast is slow:
+ # 设置一个新的指针,从头节点出发,慢指针速度为1,所以可以使用慢指针从相遇点出发
+ newptr = head
+ while newptr is not slow:
+ slow = slow.next
+ newptr = newptr.next
+ # 在环入口相遇
+ return slow
+```
+
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode147对链表进行插入排序.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode147对链表进行插入排序.md
index a21f825..2a0b700 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode147对链表进行插入排序.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode147对链表进行插入排序.md
@@ -4,11 +4,11 @@
>
> 另外希望手机阅读的同学可以来我的 [**公众号:袁厨的算法小屋**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png) 两个平台同步,想要和题友一起刷题,互相监督的同学,可以在我的小屋点击[**刷题小队**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png)进入。
-有的老哥说链表的排序搞不明白,让我写一下,一不小心给忘记了,今天咱们就安排上。没有学过数据结构的同学可以先看下这个文章
+有的老哥说链表的排序搞不明白,让我写一下,一不小心给忘记了,今天咱们就安排上。没有学过数据结构的同学可以先看下这个文章:
[【绘图解析】链表详解](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84%E5%92%8C%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95/%E5%85%B3%E4%BA%8E%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%9A%84%E9%82%A3%E4%BA%9B%E4%BA%8B.md)
-另外大家如果忘记了[【动画模拟】插入排序](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84%E5%92%8C%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95/%E7%9B%B4%E6%8E%A5%E6%8F%92%E5%85%A5%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F.md)和[【动画模拟】归并排序](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84%E5%92%8C%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95/%E5%BD%92%E5%B9%B6%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F.md)思想的话,可以先复习一下,不然这两道题目会看的云里雾里。
+另外大家如果忘记了[【动画模拟】插入排序](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84%E5%92%8C%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95/%E7%9B%B4%E6%8E%A5%E6%8F%92%E5%85%A5%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F.md)和[【动画模拟】归并排序](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84%E5%92%8C%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95/%E5%BD%92%E5%B9%B6%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F.md)思想的话,可以先复习一下,不然这两道题目会看得云里雾里。
#### [147. 对链表进行插入排序](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/insertion-sort-list/)
@@ -30,15 +30,13 @@
我们的指针在数组时,可以随意的前后移动,将指针指向值和新元素的值比较后,将新元素插入到合适的位置。
-我们知道链表查询元素的时间复杂度为 O(n),我们只能够通过遍历链表查询元素。
+我们知道链表查询元素的时间复杂度为O(n),我们只能够通过遍历链表查询元素。
-那么我们怎么才能将新元素放到合适的位置呢?
-
-**见下图**
+那么我们怎么才能将新元素放到合适的位置呢?见下图。

-此时我们不能通过移动绿色指针来寻找 5 的合适位置,那么我们应该怎么做呢?见下图
+此时我们不能通过移动绿色指针来寻找 5 的合适位置,那么我们应该怎么做呢?见下图。

@@ -54,13 +52,13 @@
下面我们再来看动画模拟具体过程。
-**注:为了更好的表达算法思想,让过程更流畅,特省略了指针的移动细节,直接插入到合适位置,后面会详细说明插入操作的具体步骤**
+**注:为了更好的表达算法思想,让过程更流畅,特省略了指针的移动细节,直接插入到合适位置,后面会详细说明插入操作的具体步骤。**

我们通过上面的动画知道了大致过程,那么我们的是如何将新元素插入到指定位置的呢?
-见下图
+见下图。
@@ -68,9 +66,9 @@
-我们想要将 3 插入到 2 和 4 的中间,此时我们三个指针分别指向 2,4,3
+我们想要将 3 插入到 2 和 4 的中间,此时我们三个指针分别指向 2,4,3。
-我们共分 4 步,来完成这个操作,见下图
+我们共分 4 步,来完成这个操作,见下图。

@@ -87,7 +85,6 @@ Java Code:
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
-
if (head == null && head.next == null) {
return head;
}
@@ -98,7 +95,6 @@ class Solution {
//判断是否需要执行插入操作
ListNode pre = head.next;
ListNode last = head;
- ListNode temphead = dummyNode;
while (pre != null) {
//不需要插入到合适位置,则继续往下移动
if (last.val <= pre.val) {
@@ -107,7 +103,7 @@ class Solution {
continue;
}
//开始出发,查找新元素的合适位置
- temphead = dummyNode;
+ ListNode temphead = dummyNode;
while (temphead.next.val <= pre.val) {
temphead = temphead.next;
}
@@ -115,10 +111,10 @@ class Solution {
last.next = pre.next;
pre.next = temphead.next;
temphead.next = pre;
+ //继续往下移动
pre = last.next;
}
return dummyNode.next;
-
}
}
```
@@ -139,7 +135,6 @@ public:
//判断是否需要执行插入操作
ListNode * pre = head->next;
ListNode * last = head;
- ListNode * temphead = dummyNode;
while (pre != nullptr) {
//不需要插入到合适位置,则继续往下移动
if (last->val <= pre->val) {
@@ -148,7 +143,7 @@ public:
continue;
}
//开始出发,查找新元素的合适位置
- temphead = dummyNode;
+ ListNode * temphead = dummyNode;
while (temphead->next->val <= pre->val) {
temphead = temphead->next;
}
@@ -156,6 +151,7 @@ public:
last->next = pre->next;
pre->next = temphead->next;
temphead->next = pre;
+ //继续往下移动
pre = last->next;
}
return dummyNode->next;
@@ -163,5 +159,71 @@ public:
};
```
+JS Code:
+
+```javascript
+var insertionSortList = function(head) {
+ if (head === null || head.next === null) return head;
+ //哑节点
+ let dummyNode = new ListNode(-1, head);
+ let pre = head.next;
+ //pre负责指向新元素,last 负责指向新元素的前一元素
+ //判断是否需要执行插入操作
+ let last = head;
+ while (pre) {
+ //不需要插入到合适位置,则继续往下移动
+ if (last.val <= pre.val) {
+ last = last.next;
+ pre = pre.next;
+ continue;
+ }
+ //开始出发,查找新元素的合适位置
+ let tempHead = dummyNode;
+ while (tempHead.next.val <= pre.val) {
+ tempHead = tempHead.next;
+ }
+ //此时我们已经找到了合适位置,我们需要进行插入,大家可以画一画
+ last.next = pre.next;
+ pre.next = tempHead.next;
+ tempHead.next = pre;
+ //继续往下移动
+ pre = last.next;
+ }
+ return dummyNode.next;
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def insertionSortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
+ if head is None or head.next is None:
+ return head
+ # 哑节点
+ dummyNode = ListNode(-1, head)
+ # pre负责指向新元素,last 负责指向新元素的前一元素
+ # 判断是否需要执行插入操作
+ pre = head.next
+ last = head
+ while pre is not None:
+ # 不需要插入到合适位置,则继续往下移动
+ if last.val <= pre.val:
+ pre = pre.next
+ last = last.next
+ continue
+ # 开始出发,查找新元素的合适位置
+ temphead = dummyNode
+ while temphead.next.val <= pre.val:
+ temphead = temphead.next
+ # 此时我们已经找到了合适位置,我们需要进行插入,大家可以画一画
+ last.next = pre.next
+ pre.next = temphead.next
+ temphead.next = pre
+ # 继续往下移动
+ pre = last.next
+ return dummyNode.next
+```
+
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode148链表排序.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode148链表排序.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e69de29..0000000
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode206反转链表.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode206反转链表.md
index 3811f23..5885b41 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode206反转链表.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode206反转链表.md
@@ -1,6 +1,12 @@
+> 如果阅读时,发现错误,或者动画不可以显示的问题可以添加我微信好友 **[tan45du_one](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/tan45du.github.io/master/个人微信.15egrcgqd94w.jpg)** ,备注 github + 题目 + 问题 向我反馈
+>
+> 感谢支持,该仓库会一直维护,希望对各位有一丢丢帮助。
+>
+> 另外希望手机阅读的同学可以来我的 [**公众号:袁厨的算法小屋**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png) 两个平台同步,想要和题友一起刷题,互相监督的同学,可以在我的小屋点击[**刷题小队**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png)进入。
+
今天咱们说一道非常简单但是很经典的面试题,思路很容易,但是里面细节挺多,所以我们还是需要注意。
-我们先来看一下题目描述
+我们先来看一下题目描述。
#### [206. 反转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
@@ -19,17 +25,15 @@
原理很容易理解,我们首先将 low 指针指向空节点, pro 节点指向 head 节点,
-然后我们定义一个临时节点指向 pro 节点,
+然后我们定义一个临时节点 temp 指向 pro 节点,
-此时我们就记住了 pro 节点的位置,然后 pro = pro.next.这样我们三个指针指向三个不同的节点。
+此时我们就记住了 pro 节点的位置,然后 pro = pro.next,这样我们三个指针指向三个不同的节点。
则我们将 temp 指针指向 low 节点,此时则完成了反转。
-反转之后我们继续反转下一节点,则
+反转之后我们继续反转下一节点,则 low = temp 即可。然后重复执行上诉操作直至最后,这样则完成了反转链表。
-low = temp 即可。然后重复执行上诉操作直至最后,这样则完成了反转链表。
-
-我们下面看代码吧
+我们下面看代码吧。
我会对每个关键点进行注释,大家可以参考动图理解。
@@ -41,15 +45,10 @@ Java Code:
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
- //特殊情况
+ //特殊情况
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
- //反转
- return reverse(head);
- }
- public ListNode reverse (ListNode head) {
-
ListNode low = null;
ListNode pro = head;
while (pro != null) {
@@ -64,42 +63,18 @@ class Solution {
}
return low;
}
-
}
```
-JS Code:
-```javascript
-var reverseList = function(head) {
- if(!head || !head.next) {
- return head;
- }
- let low = null;
- let pro = head;
- while (pro) {
- let temp = pro;
- pro = pro.next;
- temp.next = low;
- low = temp;
- }
- return low;
-};
-```
-
-C++代码
+C++ Code:
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
- //特殊情况
+ //特殊情况
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) {
return head;
}
- //反转
- return reverse(head);
- }
- ListNode * reverse (ListNode * head) {
-
ListNode * low = nullptr;
ListNode * pro = head;
while (pro != nullptr) {
@@ -117,6 +92,52 @@ public:
};
```
+JS Code:
+
+```javascript
+var reverseList = function(head) {
+ //特殊情况
+ if(!head || !head.next) {
+ return head;
+ }
+ let low = null;
+ let pro = head;
+ while (pro) {
+ //代表橙色指针
+ let temp = pro;
+ //移动绿色指针
+ pro = pro.next;
+ //反转节点
+ temp.next = low;
+ //移动黄色指针
+ low = temp;
+ }
+ return low;
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
+ # 特殊情况
+ if head is None or head.next is None:
+ return head
+ low = None
+ pro = head
+ while pro is not None:
+ # 代表橙色指针
+ temp = pro
+ # 移动绿色指针
+ pro = pro.next
+ # 反转节点
+ temp.next = low
+ # 移动黄色指针
+ low = temp
+ return low
+```
+
上面的迭代写法是不是搞懂啦,现在还有一种递归写法,不是特别容易理解,刚开始刷题的同学,可以只看迭代解法。
@@ -133,8 +154,8 @@ class Solution {
}
//保存最后一个节点
ListNode pro = reverseList(head.next);
- //将节点进行反转。我们可以这样理解 4.next.next = 4;
- //4.next = 5;
+ //将节点进行反转。我们可以这样理解 4.next.next = 4
+ //4.next = 5
//则 5.next = 4 则实现了反转
head.next.next = head;
//防止循环
@@ -142,23 +163,9 @@ class Solution {
return pro;
}
}
-
```
-JS Code:
-```javascript
-var reverseList = function(head) {
- if (!head || !head.next) {
- return head;
- }
- let pro = reverseList(head.next);
- head.next.next = head;
- head.next = null;
- return pro;
-};
-```
-
-C++代码:
+C++ Code:
```cpp
class Solution {
@@ -170,8 +177,8 @@ public:
}
//保存最后一个节点
ListNode * pro = reverseList(head->next);
- //将节点进行反转。我们可以这样理解 4->next->next = 4;
- //4->next = 5;
+ //将节点进行反转。我们可以这样理解 4->next->next = 4
+ //4->next = 5
//则 5->next = 4 则实现了反转
head->next->next = head;
//防止循环
@@ -181,3 +188,61 @@ public:
};
```
+JS Code:
+
+```javascript
+var reverseList = function(head) {
+ //结束条件
+ if (!head || !head.next) {
+ return head;
+ }
+ //保存最后一个节点
+ let pro = reverseList(head.next);
+ //将节点进行反转。我们可以这样理解 4.next.next = 4
+ //4.next = 5
+ //则 5.next = 4 则实现了反转
+ head.next.next = head;
+ //防止循环
+ head.next = null;
+ return pro;
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
+ # 结束条件
+ if head is None or head.next is None:
+ return head
+ # 保存最后一个节点
+ pro = self.reverseList(head.next)
+ # 将节点进行反转。我们可以这样理解 4->next->next = 4
+ # 4->next = 5
+ # 则 5->next = 4 则实现了反转
+ head.next.next = head
+ # 防止循环
+ head.next = None
+ return pro
+```
+
+
+
+> 贡献者[@jaredliw](https://github.com/jaredliw)注:
+>
+> 这里提供一个比较直观的递归写法供大家参考。由于代码比较直白,其它语言的我就不写啦。
+>
+> ```python
+> class Solution:
+> def reverseList(self, head: ListNode, prev_nd: ListNode = None) -> ListNode:
+> # 结束条件
+> if head is None:
+> return prev_nd
+> # 记录下一个节点并反转
+> next_nd = head.next
+> head.next = prev_nd
+> # 给定下一组该反转的节点
+> return self.reverseList(next_nd, head)
+> ```
+
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode328奇偶链表.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode328奇偶链表.md
index 83f4cd9..1b11c0e 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode328奇偶链表.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode328奇偶链表.md
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@
#### 题目解析
-题目也很容易理解就是让我们将原来奇数位的结点放一起,偶数位的结点放一起。这里需要注意,和结点值无关,是奇数位和偶数位结点。
+题目也很容易理解就是让我们将原来奇数位的结点放一起,偶数位的结点放一起。这里需要注意,题目和结点值无关,是奇数位和偶数位结点。
我们可以先将奇数位和在一起,再将偶数位和在一起,最后再将两个链表合并很简单,我们直接看动画模拟吧。
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ class Solution {
}
ListNode odd = head;
ListNode even = head.next;
- ListNode evenhead = even;
+ ListNode evenHead = even;
while (odd.next != null && even.next != null) {
//将偶数位合在一起,奇数位合在一起
@@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ class Solution {
even = even.next;
}
//链接
- odd.next = evenhead;
+ odd.next = evenHead;
return head;
}
}
@@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ public:
}
ListNode * odd = head;
ListNode * even = head->next;
- ListNode * evenhead = even;
+ ListNode * evenHead = even;
while (odd->next != nullptr && even->next != nullptr) {
//将偶数位合在一起,奇数位合在一起
@@ -83,7 +83,7 @@ public:
even = even->next;
}
//链接
- odd->next = evenhead;
+ odd->next = evenHead;
return head;
}
};
@@ -95,13 +95,36 @@ var oddEvenList = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
let odd = head, even = head.next, evenHead = even;
while(odd.next && even.next){
+ //将偶数位合在一起,奇数位合在一起
odd.next = even.next;
odd = odd.next;
even.next = odd.next;
even = even.next;
}
+ //链接
odd.next = evenHead;
return head;
};
```
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def oddEvenList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
+ if head is None or head.next is None:
+ return head
+ odd = head
+ even = head.next
+ evenHead = even
+ while odd.next is not None and even.next is not None:
+ # 将偶数位合在一起,奇数位合在一起
+ odd.next = even.next
+ odd = odd.next
+ even.next = odd.next
+ even = even.next
+ # 链接
+ odd.next = evenHead
+ return head
+```
+
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode82删除排序链表中的重复元素II.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode82删除排序链表中的重复元素II.md
index 983b3db..0768215 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode82删除排序链表中的重复元素II.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode82删除排序链表中的重复元素II.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
#### [82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/)
-题目描述
+**题目描述**
给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中没有重复出现的数字。
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@
这个题目也是利用我们的双指针思想,一个走在前面,一个在后面紧跟,前面的指针就好比是侦察兵,当发现重复节点时,后面指针停止移动,侦察兵继续移动,直到移动完重复节点,然后将该节点赋值给后节点。思路是不是很简单啊,那么我们来看一下动图模拟吧。
-注:这里为了表达更直观,所以仅显示了该链表中存在的节点
+注:这里为了表达更直观,所以仅显示了该链表中存在的节点。

@@ -46,20 +46,22 @@ Java Code:
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
- if(head == null||head.next==null){
- return head;
- }
+ //侦察兵指针
ListNode pre = head;
- ListNode low = new ListNode(0);
- low.next = pre;
- ListNode ret = new ListNode(-1);
- ret = low;
+ //创建哑节点,接上head
+ ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
+ dummy.next = head;
+ //跟随的指针
+ ListNode low = dummy;
while(pre != null && pre.next != null) {
if (pre.val == pre.next.val) {
+ //移动侦察兵指针直到找到与上一个不相同的元素
while (pre != null && pre.next != null && pre.val == pre.next.val) {
pre = pre.next;
}
+ //while循环后,pre停留在最后一个重复的节点上
pre = pre.next;
+ //连上新节点
low.next = pre;
}
else{
@@ -67,7 +69,7 @@ class Solution {
low = low.next;
}
}
- return ret.next;
+ return dummy.next;//注意,这里传回的不是head,而是虚拟节点的下一个节点,head有可能已经换了
}
}
```
@@ -78,20 +80,22 @@ C++ Code:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
- if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr){
- return head;
- }
+ //侦察兵指针
ListNode * pre = head;
- ListNode * low = new ListNode(0);
- low->next = pre;
- ListNode * ret = new ListNode(-1);
- ret = low;
+ //创建哑节点,接上head
+ ListNode * dummy = new ListNode(-1);
+ dummy->next = head;
+ //跟随的指针
+ ListNode * low = dummy;
while(pre != nullptr && pre->next != nullptr) {
if (pre->val == pre->next->val) {
+ //移动侦察兵指针直到找到与上一个不相同的元素
while (pre != nullptr && pre->next != nullptr && pre->val == pre->next->val) {
pre = pre->next;
}
+ //while循环后,pre停留在最后一个重复的节点上
pre = pre->next;
+ //连上新节点
low->next = pre;
}
else{
@@ -99,8 +103,65 @@ public:
low = low->next;
}
}
- return ret->next;
+ return dummy->next;//注意,这里传回的不是head,而是虚拟节点的下一个节点,head有可能已经换了
}
};
```
+JS Code:
+
+```javascript
+var deleteDuplicates = function(head) {
+ //侦察兵指针
+ let pre = head;
+ //创建虚拟头节点,接上head
+ let dummy = new ListNode(-1);
+ dummy.next = pre;
+ //跟随的指针
+ let low = dummy;
+ while(pre != null && pre.next != null) {
+ if (pre.val == pre.next.val) {
+ //移动侦察兵指针直到找到与上一个不相同的元素
+ while (pre != null && pre.next != null && pre.val === pre.next.val) {
+ pre = pre.next;
+ }
+ //while循环后,pre停留在最后一个重复的节点上
+ pre = pre.next;
+ //连上新节点
+ low.next = pre;
+ }
+ else{
+ pre = pre.next;
+ low = low.next;
+ }
+ }
+ return dummy.next;//注意,这里传回的不是head,而是虚拟节点的下一个节点,head有可能已经换了
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def deleteDuplicates(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
+ # 侦察兵指针
+ pre = head
+ # 创建虚拟头节点,接上head
+ dummy = ListNode(-1, head)
+ # 跟随的指针
+ low = dummy
+ while pre is not None and pre.next is not None:
+ if pre.val == pre.next.val:
+ # 移动侦察兵指针直到找到与上一个不相同的元素
+ while pre is not None and pre.next is not None and pre.val == pre.next.val:
+ pre = pre.next
+ # while循环后,pre停留在最后一个重复的节点上
+ pre = pre.next
+ # 连上新节点
+ low.next = pre
+ else:
+ pre = pre.next
+ low = low.next
+ return dummy.next # 注意,这里传回的不是head,而是虚拟节点的下一个节点,head有可能已经换了
+```
+
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode86分隔链表.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode86分隔链表.md
index 6412931..4147a75 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode86分隔链表.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode86分隔链表.md
@@ -37,31 +37,20 @@
Java Code:
```java
-/**
- * Definition for singly-linked list.
- * public class ListNode {
- * int val;
- * ListNode next;
- * ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
- * }
- */
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
- if (head == null) {
- return head;
- }
ListNode pro = head;
ListNode big = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode small = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode headbig = big;
- ListNode headsmall =small;
- //分
- while (pro != null) {
+ ListNode headsmall = small;
+ //分
+ while (pro != null) {
//大于时,放到 big 链表上
if (pro.val >= x) {
big.next = pro;
big = big.next;
- // 小于放到 small 链表上
+ //小于时,放到 small 链表上
}else {
small.next = pro;
small = small.next;
@@ -83,21 +72,18 @@ C++ Code:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
- if (head == nullptr) {
- return head;
- }
ListNode * pro = head;
ListNode * big = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode * small = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode * headbig = big;
- ListNode * headsmall =small;
- //分
- while (pro != nullptr) {
+ ListNode * headsmall = small;
+ //分
+ while (pro != nullptr) {
//大于时,放到 big 链表上
if (pro->val >= x) {
big->next = pro;
big = big->next;
- // 小于放到 small 链表上
+ //小于时,放到 small 链表上
}else {
small->next = pro;
small = small->next;
@@ -113,5 +99,61 @@ public:
};
```
+JS Code:
+```js
+var partition = function(head, x) {
+ let pro = head;
+ let big = new ListNode(-1);
+ let small = new ListNode(-1);
+ let headbig = big;
+ let headsmall = small;
+ //分
+ while (pro) {
+ //大于时,放到 big 链表上
+ if (pro.val >= x) {
+ big.next = pro;
+ big = big.next;
+ //小于时,放到 small 链表上
+ }else {
+ small.next = pro;
+ small = small.next;
+ }
+ pro = pro.next;
+ }
+ //细节
+ big.next = null;
+ //合
+ small.next = headbig.next;
+ return headsmall.next;
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def partition(self, head: ListNode, x: int) -> ListNode:
+ pro = head
+ big = ListNode(-1)
+ small = ListNode(-1)
+ headbig = big
+ headsmall = small
+ # 分
+ while pro is not None:
+ # 大于时,放到 big 链表上
+ if pro.val >= x:
+ big.next = pro
+ big = big.next
+ # 小于时,放到 small 链表上
+ else:
+ small.next = pro
+ small = small.next
+ pro = pro.next
+ # 细节
+ big.next = None
+ # 合
+ small.next = headbig.next
+ return headsmall.next
+```
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode92反转链表2.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode92反转链表2.md
index 13b3af2..93b90b6 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode92反转链表2.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode92反转链表2.md
@@ -4,14 +4,12 @@
>
> 另外希望手机阅读的同学可以来我的 [**公众号:袁厨的算法小屋**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png) 两个平台同步,想要和题友一起刷题,互相监督的同学,可以在我的小屋点击[**刷题小队**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png)进入。
-今天我们来说一下反转链表 2,其实这个和 1 的思路差不多,今天先说一个比较好理解的方法,完全按照反转链表 1 的方法来解决,大家看这个题目之前要先看一下[【动画模拟】leetcode 206 反转链表](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/leetcode206%E5%8F%8D%E8%BD%AC%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8.md)
+今天我们来说一下反转链表 2,其实这个和 1 的思路差不多,今天先说一个比较好理解的方法,完全按照反转链表 1 的方法来解决,大家看这个题目之前要先看一下[【动画模拟】leetcode 206 反转链表](https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base/blob/main/animation-simulation/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%AF%87/leetcode206%E5%8F%8D%E8%BD%AC%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8.md)。
下面我们先来看一下题目。
#### [92. 反转链表 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/)
-难度中等836
-
给你单链表的头指针 `head` 和两个整数 `left` 和 `right` ,其中 `left <= right` 。请你反转从位置 `left` 到位置 `right` 的链表节点,返回 **反转后的链表** 。
**示例 1:**
@@ -43,7 +41,6 @@ Java Code:
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
-
//虚拟头节点
ListNode temp = new ListNode(-1);
temp.next = head;
@@ -53,26 +50,28 @@ class Solution {
for (; i < left-1; ++i) {
pro = pro.next;
}
- // 保存 left 节点前的第一个节点
+ //保存 left 节点前的一个节点
ListNode leftNode = pro;
+ //来到 right 节点
for (; i < right; ++i) {
pro = pro.next;
}
- // 保存 right 节点后的节点
+ //保存 right 节点后的一个节点
ListNode rightNode = pro.next;
//切断链表
- pro.next = null;
- ListNode newhead = leftNode.next;
- leftNode.next = null;
- leftNode.next = rever(newhead);
+ pro.next = null;//切断 right 后的部分
+ ListNode newhead = leftNode.next;//保存 left 节点
+ leftNode.next = null;//切断 left 前的部分
+ //反转
+ leftNode.next = reverse(newhead);
//重新接头
newhead.next = rightNode;
return temp.next;
}
//和反转链表1代码一致
- public ListNode rever (ListNode head) {
- ListNode low = null;
+ public ListNode reverse (ListNode head) {
+ ListNode low = null;
ListNode pro = head;
while (pro != null) {
ListNode temp = pro;
@@ -91,6 +90,7 @@ C++ Code:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {
+ //虚拟头节点
ListNode * temp = new ListNode(-1);
temp->next = head;
ListNode * pro = temp;
@@ -99,23 +99,26 @@ public:
for (; i < left-1; ++i) {
pro = pro->next;
}
- // 保存 left 节点前的第一个节点
+ //保存 left 节点前的一个节点
ListNode * leftNode = pro;
+ //来到 right 节点
for (; i < right; ++i) {
pro = pro->next;
}
- // 保存 right 节点后的节点
+ //保存 right 节点后的一个节点
ListNode * rightNode = pro->next;
//切断链表
- pro->next = nullptr;
- ListNode * newhead = leftNode->next;
- leftNode->next = nullptr;
- leftNode->next = rever(newhead);
+ pro->next = nullptr;//切断 right 后的部分
+ ListNode * newhead = leftNode->next;//保存 left 节点
+ leftNode->next = nullptr;//切断 left 前的部分
+ //反转
+ leftNode->next = reverse(newhead);
//重新接头
newhead->next = rightNode;
return temp->next;
}
- ListNode * rever (ListNode * head) {
+ //和反转链表1代码一致
+ ListNode * reverse (ListNode * head) {
ListNode * low = nullptr;
ListNode * pro = head;
while (pro != nullptr) {
@@ -129,3 +132,89 @@ public:
};
```
+JS Code:
+
+```js
+var reverseBetween = function(head, left, right) {
+ //虚拟头节点
+ let temp = new ListNode(-1);
+ temp.next = head;
+ let pro = temp;
+ //来到 left 节点前的一个节点
+ let i = 0;
+ for (; i < left-1; ++i) {
+ pro = pro.next;
+ }
+ //保存 left 节点前的一个节点
+ let leftNode = pro;
+ //来到 right 节点
+ for (; i < right; ++i) {
+ pro = pro.next;
+ }
+ //保存 right 节点后的一个节点
+ let rightNode = pro.next;
+ //切断链表
+ pro.next = null;//切断 right 后的部分
+ let newhead = leftNode.next;//保存 left 节点
+ leftNode.next = null;//切断 left 前的部分
+ //反转
+ leftNode.next = reverse(newhead);
+ //重新接头
+ newhead.next = rightNode;
+ return temp.next;
+};
+
+//和反转链表1代码一致
+var reverse = function(head) {
+ let low = null;
+ let pro = head;
+ while (pro) {
+ let temp = pro;
+ pro = pro.next;
+ temp.next = low;
+ low = temp;
+ }
+ return low;
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def reverseBetween(self, head: ListNode, left: int, right: int) -> ListNode:
+ # 虚拟头节点
+ temp = ListNode(-1)
+ temp.next = head
+ pro = temp
+ # 来到 left 节点前的一个节点
+ for _ in range(left - 1):
+ pro = pro.next
+ # 保存 left 节点前的第一个节点
+ leftNode = pro
+ for _ in range(right - left + 1):
+ pro = pro.next
+ # 保存 right 节点后的节点
+ rightNode = pro.next
+ # 切断链表
+ pro.next = None # 切断 right 后的部分
+ newhead = leftNode.next # 保存 left 节点
+ leftNode.next = None # 切断 left 前的部分
+ # 反转
+ leftNode.next = self.reverse(newhead)
+ # 重新接头
+ newhead.next = rightNode
+ return temp.next
+
+ # 和反转链表1代码一致
+ def reverse(self, head):
+ low = None
+ pro = head
+ while pro is not None:
+ temp = pro
+ pro = pro.next
+ temp.next = low
+ low = temp
+ return low
+```
+
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode相交链表.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode相交链表.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 2f84214..0000000
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/leetcode相交链表.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,172 +0,0 @@
-> 如果阅读时,发现错误,或者动画不可以显示的问题可以添加我微信好友 **[tan45du_one](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/tan45du.github.io/master/个人微信.15egrcgqd94w.jpg)** ,备注 github + 题目 + 问题 向我反馈
->
-> 感谢支持,该仓库会一直维护,希望对各位有一丢丢帮助。
->
-> 另外希望手机阅读的同学可以来我的 [**公众号:袁厨的算法小屋**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png) 两个平台同步,想要和题友一起刷题,互相监督的同学,可以在我的小屋点击[**刷题小队**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png)进入。
-
-#### [160. 相交链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/)
-
-### 前言
-
-今天给大家带来一个不是那么难的题目,这个题目的解答方法很多,只要能AC的就是好方法,虽然题目不是特别难但是也是剑指offer上的经典题目所以大家要记得打卡呀。
-
-然后今天我们的链表板块就算结束啦。周末的时候我会对链表的题目做一个总结,俗话说温故而知新嘛。好啦废话不多说,我们一起来看一下今天的题目吧
-
-题目描述:
-
-输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共节点。如下图,返回黄色结点即可。
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-题目表达是不是也很简单,这个题目我的方法一共有两个,一种就是用HashSet进行存储,一种就是利用双指针,大家有更好的可以在下面讨论呀。
-
-### HashSet
-
-这个方法是比较简单的,主要思路就是,先遍历一个链表将链表的所有值都存到Hashset中,然后再遍历另一个链表,如果发现某个结点在Hashset中已经存在那我们直接返回该节点即可,代码也很简单。
-
-**题目代码**
-
-Java Code:
-
-```java
-public class Solution {
- public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
- ListNode tempa = headA;
- ListNode tempb = headB;
- //定义Hashset
- HashSet arr = new HashSet();
- while (tempa != null) {
- arr.add(tempa);
- tempa = tempa.next;
- }
- while (tempb != null) {
- if (arr.contains(tempb)) {
- return tempb;
- }
- tempb = tempb.next;
- }
- return tempb;
- }
-}
-```
-
-C++ Code:
-
-```cpp
-class Solution {
-public:
- ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
- ListNode * tempa = headA;
- ListNode * tempb = headB;
- //定义Hashset, cpp对应set
- set arr;
- while (tempa != nullptr) {
- arr.insert(tempa);
- tempa = tempa->next;
- }
- while (tempb != nullptr) {
- if (arr.find(tempb) != arr.end()) {
- return tempb;
- }
- tempb = tempb->next;
- }
- return tempb;
- }
-};
-```
-
-JS Code:
-```javascript
-var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
- let tempa = headA, tempb = headB
- const map = new Map()
- while(tempa){
- map.set(tempa, 1)
- tempa = tempa.next
- }
- while(tempb){
- if(map.get(tempb))
- return tempb
- tempb = tempb.next
- }
- return tempb
-};
-```
-
-下面这个方法比较巧妙,不是特别容易想到,大家可以自己实现一下,这个方法也是利用我们的双指针思想。
-
-下面我们直接看动图吧,特别直观,一下就可以搞懂。
-
-
-
-是不是一下就懂了呀,我们利用双指针,当某一指针遍历完链表之后,然后掉头去另一个链表的头部,继续遍历。因为速度相同所以他们第二次遍历的时候肯定会相遇,是不是很浪漫啊!
-
-**题目代码**
-
-Java Code:
-
-```java
-public class Solution {
- public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
- //定义两个节点
- ListNode tempa = headA;
- ListNode tempb = headB;
- //循环
- while (tempa != tempb) {
- //如果不为空就指针下移,为空就跳到另一链表的头部
- tempa = tempa != null ? tempa.next:headB;
- tempb = tempb != null ? tempb.next:headA;
- }
- return tempa;
- }
-}
-```
-
-C++ Code:
-
-```cpp
-class Solution {
-public:
- ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
- //定义两个节点
- ListNode * tempa = headA;
- ListNode * tempb = headB;
- //循环
- while (tempa != tempb) {
- //如果不为空就指针下移,为空就跳到另一链表的头部
- tempa = tempa != nullptr ? tempa->next: headB;
- tempb = tempb != nullptr ? tempb->next: headA;
- }
- return tempa;
- }
-};
-```
-
-JS Code:
-```javascript
-var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
- let tempa = headA, tempb = headB
- while(tempa !== tempb){
- tempa = tempa ? tempa.next : headB
- tempb = tempb ? tempb.next : headA
- }
- return tempa
-};
-```
-
-好啦,链表的题目就结束啦,希望大家能有所收获,下周就要更新新的题型啦,继续坚持,肯定会有收获的。
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/剑指Offer25合并两个排序的链表.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/剑指Offer25合并两个排序的链表.md
index 7f03b6c..cbe9b75 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/剑指Offer25合并两个排序的链表.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/剑指Offer25合并两个排序的链表.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
#### [剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/he-bing-liang-ge-pai-xu-de-lian-biao-lcof/)
-将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
+将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 **升序** 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
@@ -15,11 +15,11 @@
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
```
-今天的题目思路很简单,但是一遍AC也是不容易的。链表大部分题目考察的都是考生代码的完整性和鲁棒性,所以有些题目我们看着思路很简单,但是想直接通过还是需要下一翻工夫的,所以建议大家将所有链表的题目都自己写一下。实在没有时间做的同学,可以自己在脑子里打一遍代码,想清没一行代码的作用。
+今天的题目思路很简单,但是一遍AC也是不容易的。链表大部分题目考察的都是考生代码的完整性和鲁棒性,所以有些题目我们看着思路很简单,但是想直接通过还是需要下一翻工夫的,所以建议大家将所有链表的题目都自己写一下。实在没有时间做的同学,可以自己在脑子里打一遍代码,想清每一行代码的作用。
迭代法:
-因为我们有两个升序链表,我们需要将其合并,那么我们需要创建一个新节点headpre,然后我们利用双指针思想,每个链表放置一个指针,然后进行遍历并对比当前指针指向的值。然后headpre.next指向较小值的那个节点,不断迭代,直至到达某一有序链表底部,此时一个链表遍历完成,然后我们将未完全遍历的链表接在我们接在合并链表之后即可。
+因为我们有两个升序链表,我们需要将其合并,那么我们需要创建一个新节点 headpre,然后我们利用双指针思想,每个链表放置一个指针,然后进行遍历并对比当前指针指向的值。然后 headpre.next 指向较小值的那个节点,不断迭代,直至到达某一有序链表底部,此时一个链表遍历完成,然后我们将未完全遍历的链表接在我们接在合并链表之后即可。
这是我们迭代做法,另外这个题目还有一个递归方法,目前先不写,等链表掌握差不多的时候会单独写一篇关于递归的文章,也算是为树的题目做铺垫。
@@ -80,3 +80,46 @@ public:
};
```
+JS Code:
+
+```js
+var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
+ let headpro = new ListNode(-1);
+ let headtemp = headpro;
+ while (l1 && l2) {
+ //接上大的那个
+ if (l1.val >= l2.val) {
+ headpro.next = l2;
+ l2 = l2.next;
+ }
+ else {
+ headpro.next = l1;
+ l1 = l1.next;
+ }
+ headpro = headpro.next;
+ }
+ headpro.next = l1 != null ? l1:l2;
+ return headtemp.next;
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
+ headpro = ListNode(-1)
+ headtemp = headpro
+ while l1 and l2:
+ # 接上大的那个
+ if l1.val >= l2.val:
+ headpro.next = l2
+ l2 = l2.next
+ else:
+ headpro.next = l1
+ l1 = l1.next
+ headpro = headpro.next
+ headpro.next = l1 if l1 is not None else l2
+ return headtemp.next
+```
+
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/剑指Offer52两个链表的第一个公共节点.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/剑指Offer52两个链表的第一个公共节点.md
index d045c60..c51ab29 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/剑指Offer52两个链表的第一个公共节点.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/剑指Offer52两个链表的第一个公共节点.md
@@ -4,13 +4,13 @@
>
> 另外希望手机阅读的同学可以来我的 [**公众号:袁厨的算法小屋**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png) 两个平台同步,想要和题友一起刷题,互相监督的同学,可以在我的小屋点击[**刷题小队**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png)进入。
-#### [剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/liang-ge-lian-biao-de-di-yi-ge-gong-gong-jie-dian-lcof/)
+#### [剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/liang-ge-lian-biao-de-di-yi-ge-gong-gong-jie-dian-lcof/) & [160. 相交链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/)
### 前言
今天给大家带来一个不是那么难的题目,这个题目的解答方法很多,只要能AC的就是好方法,虽然题目不是特别难但是也是剑指offer上的经典题目所以大家要记得打卡呀。
-然后今天我们的链表板块就算结束啦。周末的时候我会对链表的题目做一个总结,俗话说温故而知新嘛。好啦废话不多说,我们一起来看一下今天的题目吧
+然后今天我们的链表板块就算结束啦。周末的时候我会对链表的题目做一个总结,俗话说温故而知新嘛。好啦废话不多说,我们一起来看一下今天的题目吧!
题目描述:
@@ -41,16 +41,19 @@ public class Solution {
ListNode tempb = headB;
//定义Hashset
HashSet arr = new HashSet();
+ //遍历链表A,将所有值都存到arr中
while (tempa != null) {
arr.add(tempa);
tempa = tempa.next;
}
+ //遍历列表B,如果发现某个结点已在arr中则直接返回该节点
while (tempb != null) {
if (arr.contains(tempb)) {
return tempb;
}
tempb = tempb.next;
}
+ //若上方没有返回,此刻tempb为null
return tempb;
}
@@ -67,21 +70,73 @@ public:
ListNode * tempb = headB;
//定义Hashset
set arr;
+ //遍历链表A,将所有值都存到arr中
while (tempa != nullptr) {
arr.insert(tempa);
tempa = tempa->next;
}
+ //遍历列表B,如果发现某个结点已在arr中则直接返回该节点
while (tempb != nullptr) {
if (arr.find(tempb) != arr.end()) {
return tempb;
}
tempb = tempb->next;
}
+ //若上方没有返回,此刻tempb为null
return tempb;
}
};
```
+JS Code:
+
+```js
+var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
+ let tempa = headA;
+ let tempb = headB;
+ //定义Hashset
+ let arr = new Set();
+ //遍历链表A,将所有值都存到arr中
+ while (tempa) {
+ arr.add(tempa);
+ tempa = tempa.next;
+ }
+ //遍历列表B,如果发现某个结点已在arr中则直接返回该节点
+ while (tempb) {
+ if (arr.has(tempb)) {
+ return tempb;
+ }
+ tempb = tempb.next;
+ }
+ //若上方没有返回,此刻tempb为null
+ return tempb;
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
+ tempa = headA
+ tempb = headB
+ # 定义Hashset
+ arr = set()
+ # 遍历链表A,将所有值都存到arr中
+ while tempa is not None:
+ arr.add(tempa)
+ tempa = tempa.next
+ # 遍历列表B,如果发现某个结点已在arr中则直接返回该节点
+ while tempb is not None:
+ if tempb in arr:
+ return tempb
+ tempb = tempb.next
+ # 若上方没有返回,此刻tempb为null
+ return tempb
+```
+
+
+
下面这个方法比较巧妙,不是特别容易想到,大家可以自己实现一下,这个方法也是利用我们的双指针思想。
下面我们直接看动图吧,特别直观,一下就可以搞懂。
@@ -108,7 +163,7 @@ public class Solution {
tempa = tempa != null ? tempa.next: headB;
tempb = tempb != null ? tempb.next: headA;
}
- return tempa;
+ return tempa;//返回tempb也行
}
}
```
@@ -124,20 +179,58 @@ public:
ListNode * tempb = headB;
//循环
while (tempa != tempb) {
- //如果不为空就指针下移,为空就跳到另一链表的头部
+ //如果不为空就指针下移,为空就跳到另一链表的头部
tempa = tempa != nullptr ? tempa->next: headB;
tempb = tempb != nullptr ? tempb->next: headA;
}
- return tempa;
+ return tempa;//返回tempb也行
}
};
```
+JS Code:
+
+```js
+var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
+ //定义两个节点
+ let tempa = headA;
+ let tempb = headB;
+ //循环
+ while (tempa != tempb) {
+ //如果不为空就指针下移,为空就跳到另一链表的头部
+ tempa = tempa != null ? tempa.next: headB;
+ tempb = tempb != null ? tempb.next: headA;
+ }
+ return tempa;//返回tempb也行
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
+ # 定义两个节点
+ tempa = headA
+ tempb = headB
+ # 循环
+ while tempa is not tempb:
+ # 如果不为空就指针下移,为空就跳到另一链表的头部
+ tempa = tempa.next if tempa is not None else headB
+ tempb = tempb.next if tempb is not None else headA
+ return tempa # 返回tempb也行
+```
+
好啦,链表的题目就结束啦,希望大家能有所收获,下周就要更新新的题型啦,继续坚持,肯定会有收获的。
-
-
-
+
+
+> 贡献者[@jaredliw](https://github.com/jaredliw)注:
+>
+> 在这里带大家来看看一些其他的解题方法,虽然没有双指针有效,但还是值得一试。
+>
+> 1. 两个链表各遍历一次,找出长度。根据长度差k,让较长的那个链表先走k步。之后再两个指针一起走,由于起点一样,两个指针必将一起到达公共节点。
+> 2. 将其中一条链表的头和尾相连,公共节点就是环的入口,直接套用之前学过的算法就可以啦。(这解法看得我拍腿叫好)
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/剑指offer22倒数第k个节点.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/剑指offer22倒数第k个节点.md
index 2666add..5dc879c 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/剑指offer22倒数第k个节点.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/剑指offer22倒数第k个节点.md
@@ -12,13 +12,13 @@
题目分析:
-自己思考一下
+自己思考一下:
我们遇到这个题目,可能会有什么答题思路呢?
你看我说的对不对,是不是会想到先遍历一遍链表知道 链表节点的个数,然后再计算出倒数第n个节点。
-比如链表长度为10,倒数第3个节点,不就是正数第8个节点呀,这种方法当然可以啦,是可以实现的,那么我们再思考一下有没有其他方法呢?哦,对,我们可以将链表元素保存到数组里面,然后直接就可以知道倒数第K个节点了。这个方法确实比刚才那个方法省时间了,但是所耗的空间更多了,那我们还有什么方法吗?
+比如链表长度为10,倒数第3个节点,不就是正数第8个节点呀,这种方法当然可以啦,是可以实现的,那么我们再思考一下有没有其他方法呢?哦,对,我们可以将链表元素保存到数组里面,然后直接就可以知道倒数第k个节点了。这个方法确实比刚才那个方法省时间了,但是所耗的空间更多了,那我们还有什么方法吗?
我们可以继续利用我们的双指针呀,但是我们应该怎么做呢?
@@ -96,15 +96,43 @@ public:
JS Code:
```javascript
var getKthFromEnd = function(head, k) {
+ //特殊情况
if(!head) return head;
+ //初始化两个指针, 定义指针指向
let pro = head, after = head;
+ //先移动绿指针到指定位置
for(let i = 0; i < k - 1; i++){
pro = pro.next;
}
+ //两个指针同时移动
while(pro.next){
pro = pro.next;
after = after.next;
}
+ //返回倒数第k个节点
return after;
};
-```
\ No newline at end of file
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def getKthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode:
+ # 特殊情况
+ if head is None:
+ return head
+ # 初始化两个指针, 定义指针指向
+ pro = head
+ after = head
+ # 先移动绿指针到指定位置
+ for _ in range(k - 1):
+ pro = pro.next
+ # 两个指针同时移动
+ while pro.next is not None:
+ pro = pro.next
+ after = after.next
+ # 返回倒数第k个节点
+ return after
+```
+
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/面试题 02.03. 链表中间节点.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/面试题 02.03. 链表中间节点.md
index a1bffb0..1eda138 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/面试题 02.03. 链表中间节点.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/面试题 02.03. 链表中间节点.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
#### [876. 链表的中间结点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/)
-给定一个头结点为 head的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。
+给定一个头结点为 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。
如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@
输出:3
```
-> 说明:因为只有一个中间节点
+> 说明:因为只有一个中间节点。
**示例 2:**
@@ -26,9 +26,9 @@
输出:4
```
-> 说明:有两个中间节点所以返回后面那个
+> 说明:有两个中间节点所以返回后面那个。
-## 题目解析:
+**题目解析:**
又精心筛选了一个题目,本来想写一下删除节点的题目,然后发现这个题目更符合目前的节奏,所以先写一下这个题目,明天再给大家写删除节点的题目。
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@
一个指针走的快,一个指针走的慢,这个题目我们可以让快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,当快指针到达链表尾部的时候,慢指针不就到达中间节点了吗?
-链表中节点的个数有可能为奇数也有可能为偶数,这是两种情况,但是我们输出是相同的,那就是输出slow指针指向的节点
+链表中节点的个数有可能为奇数也有可能为偶数,这是两种情况,但是我们输出是相同的,那就是输出 slow 指针指向的节点,也就是两个中间节点的第二个。
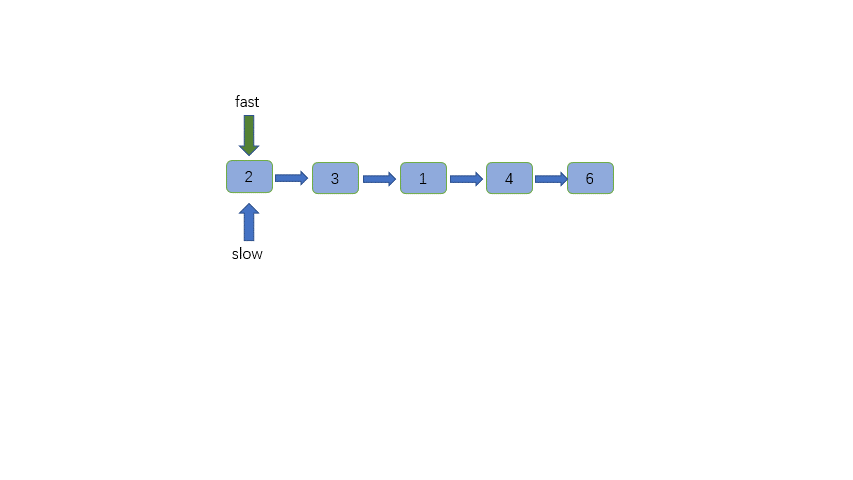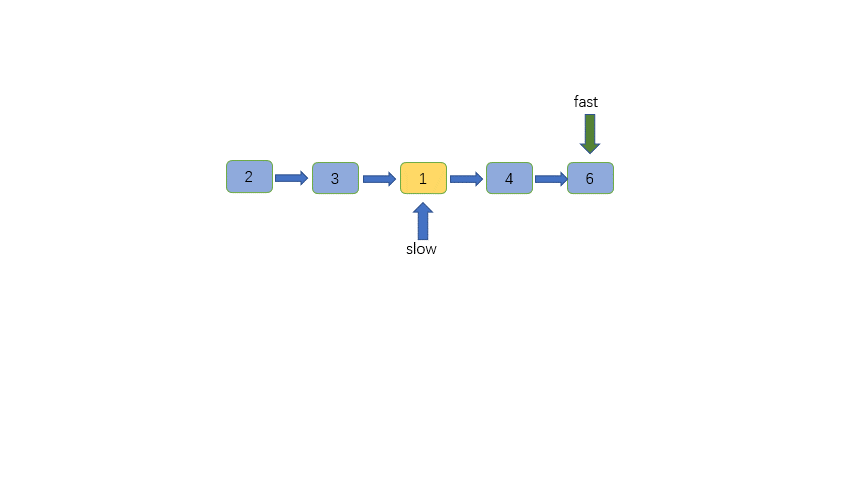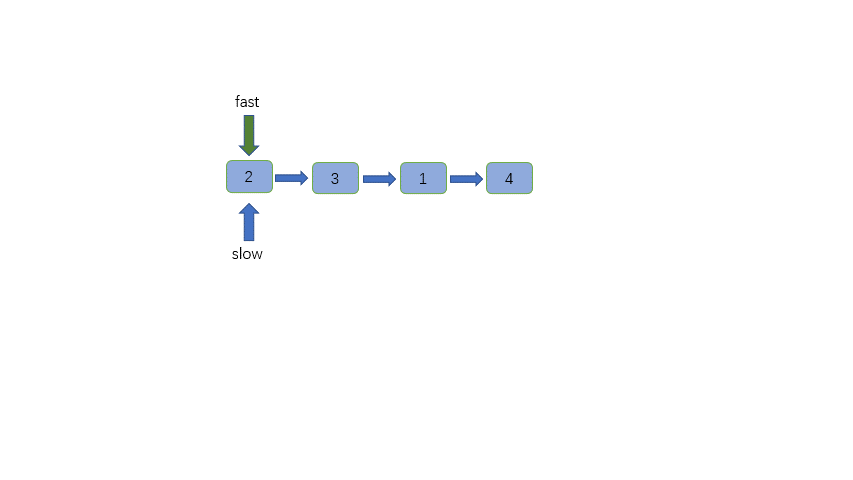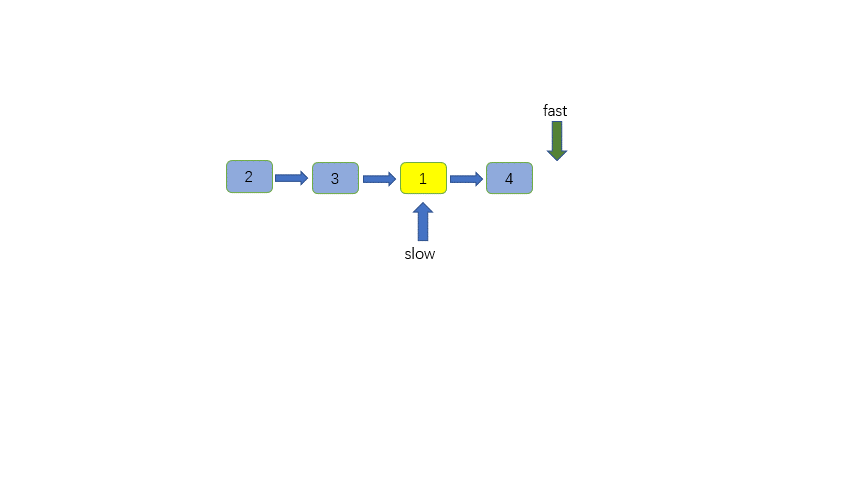
@@ -71,6 +71,7 @@ class Solution {
C++ Code:
```cpp
+class Solution {
public:
ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head) {
ListNode * fast = head;//快指针
@@ -86,3 +87,34 @@ public:
};
```
+JS Code:
+
+```js
+var middleNode = function(head) {
+ let fast = head;//快指针
+ let slow = head;//慢指针
+ //循环条件,思考一下跳出循环的情况
+ while (fast && fast.next) {
+ fast = fast.next.next;
+ slow = slow.next;
+ }
+ //返回slow指针指向的节点
+ return slow
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def middleNode(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
+ fast = head # 快指针
+ slow = head # 慢指针
+ # 循环条件,思考一下跳出循环的情况
+ while fast is not None and fast.next is not None:
+ fast = fast.next.next
+ slow = slow.next
+ # 返回slow指针指向的节点
+ return slow
+```
+
diff --git a/animation-simulation/链表篇/面试题 02.05. 链表求和.md b/animation-simulation/链表篇/面试题 02.05. 链表求和.md
index af5aa66..0865cb1 100644
--- a/animation-simulation/链表篇/面试题 02.05. 链表求和.md
+++ b/animation-simulation/链表篇/面试题 02.05. 链表求和.md
@@ -23,22 +23,22 @@
示例1:
```java
-输入:(7 -> 1 -> 6) + (5 -> 9 -> 2),即617 + 295
-输出:2 -> 1 -> 9,即912
+输入:(7 -> 1 -> 6) + (5 -> 9 -> 2),即 617 + 295
+输出:2 -> 1 -> 9,即 912
```
示例2:
```java
-输入:(9 -> 9) + (9 -> 9),即99+99
-输出:8->9->1
+输入:(9 -> 9) + (9 -> 9),即 99 + 99
+输出:8 -> 9 -> 1
```
示例3:
```java
-输入:(5)+(5),即5+5
-输出:0->1
+输入:(5) + (5),即 5 + 5
+输出:0 -> 1
```
**题目解析:**
@@ -55,11 +55,11 @@
了解了思路,但是想完全实现代码也不是特别容易,这里需要注意的三个点就是,
-1.我们需要根据两个链表的长度,不断对新链表添加节点
+1. 我们需要根据两个链表的长度,不断对新链表添加节点。
-2.需要创建一个变量用来保存进位值。
+2. 需要创建一个变量用来保存进位值。
-3.当跳出循环之后,需要根据进位值来判断需不需要再对链表长度加1.
+3. 当跳出循环之后,需要根据进位值来判断需不需要再对链表长度加1。
这三条可以结合代码理解进行。
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@

-注:这里需要注意得时,链表遍历结束,我们应该跳出循环,但是我们的nlist仍在尾部添加了1节点,那是因为跳出循环时,summod值为1,所以我们需要在尾部再添加一个节点。
+注:这里需要注意得时,链表遍历结束,我们应该跳出循环,但是我们的 nlist 仍在尾部添加了1节点,那是因为跳出循环时,summod 值为1,所以我们需要在尾部再添加一个节点。
@@ -78,8 +78,8 @@ Java Code:
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
- //返回链表
- ListNode nList = new ListNode(-1);
+ //待会儿要返回的链表
+ ListNode nList = new ListNode(-1);//哑节点
ListNode tempnode = nList;
//用来保存进位值,初始化为0
int summod = 0;
@@ -92,7 +92,7 @@ class Solution {
int sum = l1num+l2num+summod;
//更新进位值,例18/10=1,9/10=0
summod = sum/10;
- //新节点保存的值,18 % 8=2,则添加2
+ //新节点保存的值,18%8=2,则添加2
sum = sum%10;
//添加节点
tempnode.next = new ListNode(sum);
@@ -106,10 +106,10 @@ class Solution {
}
}
//最后根据进位值判断需不需要继续添加节点
- if (summod == 1) {
+ if (summod != 0) {
tempnode.next = new ListNode(summod);
}
- return nList.next;
+ return nList.next;//去除哑节点
}
}
```
@@ -120,8 +120,8 @@ C++ Code:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
- //返回链表
- ListNode * nList = new ListNode(-1);
+ //待会儿要返回的链表
+ ListNode * nList = new ListNode(-1);//哑节点
ListNode * tempnode = nList;
//用来保存进位值,初始化为0
int summod = 0;
@@ -134,7 +134,7 @@ public:
int sum = l1num + l2num + summod;
//更新进位值,例18/10=1,9/10=0
summod = sum / 10;
- //新节点保存的值,18 % 8=2,则添加2
+ //新节点保存的值,18%8=2,则添加2
sum = sum % 10;
//添加节点
tempnode->next = new ListNode(sum);
@@ -148,11 +148,85 @@ public:
}
}
//最后根据进位值判断需不需要继续添加节点
- if (summod == 1) {
+ if (summod != 0) {
tempnode->next = new ListNode(summod);
}
- return nList->next;
+ return nList->next;//哑节点
}
};
```
+JS Code:
+
+```js
+var addTwoNumbers = function(l1, l2) {
+ //待会儿要返回的链表
+ let nList = new ListNode(-1);//哑节点
+ let tempnode = nList;
+ //用来保存进位值,初始化为0
+ let summod = 0;
+ while (l1 || l2) {
+ //如果l1的链表为空则l1num为0,若是不为空,则为链表的节点值
+ //判断是否为空,为空就设为0
+ let l1num = l1 === null ? 0 : l1.val;
+ let l2num = l2 === null ? 0 : l2.val;
+ //将链表的值和进位值相加,得到为返回链表的值
+ let sum = l1num + l2num + summod;
+ //更新进位值,例18/10=1,9/10=0
+ summod = ~~(sum / 10);
+ //新节点保存的值,18%8=2,则添加2
+ sum = sum % 10;
+ //添加节点
+ tempnode.next = new ListNode(sum);
+ //移动指针
+ tempnode = tempnode.next;
+ if (l1) {
+ l1 = l1.next;
+ }
+ if (l2) {
+ l2 = l2.next;
+ }
+ }
+ //最后根据进位值判断需不需要继续添加节点
+ if (summod !== 0) {
+ tempnode.next = new ListNode(summod);
+ }
+ return nList.next;//去除哑节点
+};
+```
+
+Python Code:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
+ # 待会儿要返回的链表
+ nList = ListNode(-1) # 哑节点
+ tempnode = nList
+ # 用来保存进位值,初始化为0
+ summod = 0
+ while l1 is not None o l2 is not None:
+ # 如果l1的链表为空则l1num为0,若是不为空,则为链表的节点值
+ # 判断是否为空,为空就设为0
+ l1num = 0 if l1 is None else l1.val
+ l2num = 0 if l2 is None else l2.val
+ # 将链表的值和进位值相加,得到为返回链表的值
+ sum_ = l1num + l2num + summod
+ # 更新进位值,例18/10=1,9/10=0
+ # 新节点保存的值,1 %8=2,则添加2
+ # 注:这里使用divmod函数,对上方的代码进行了一丢丢的简化
+ summod, sum_ = divmod(sum_, 10)
+ # 添加节点
+ tempnode.next = ListNode(sum_)
+ # 移动指针
+ tempnode = tempnode.next
+ if l1 is not None:
+ l1 = l1.next
+ if l2 is not None:
+ l2 = l2.next
+ # 最后根据进位值判断需不需要继续添加节点
+ if summod != 0:
+ tempnode.next = ListNode(summod)
+ return nList.next # 去除哑节点
+```
+

