> 如果阅读时,发现错误,或者动画不可以显示的问题可以添加我微信好友 **[tan45du_one](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/tan45du.github.io/master/个人微信.15egrcgqd94w.jpg)** ,备注 github + 题目 + 问题 向我反馈
>
> 感谢支持,该仓库会一直维护,希望对各位有一丢丢帮助。
>
> 另外希望手机阅读的同学可以来我的 [**公众号:袁厨的算法小屋**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png) 两个平台同步,想要和题友一起刷题,互相监督的同学,可以在我的小屋点击[**刷题小队**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png)进入。
#### [86. 分隔链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-list/)
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个特定值 x ,请你对链表进行分隔,使得所有 小于 x 的节点都出现在 大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
你应当 保留 两个分区中每个节点的初始相对位置。
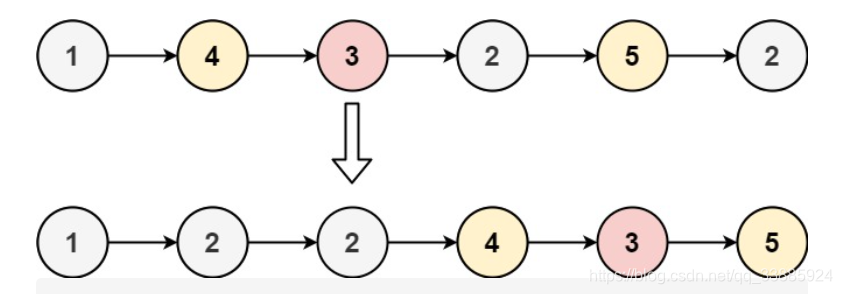
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3
输出:[1,2,2,4,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [2,1], x = 2
输出:[1,2]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
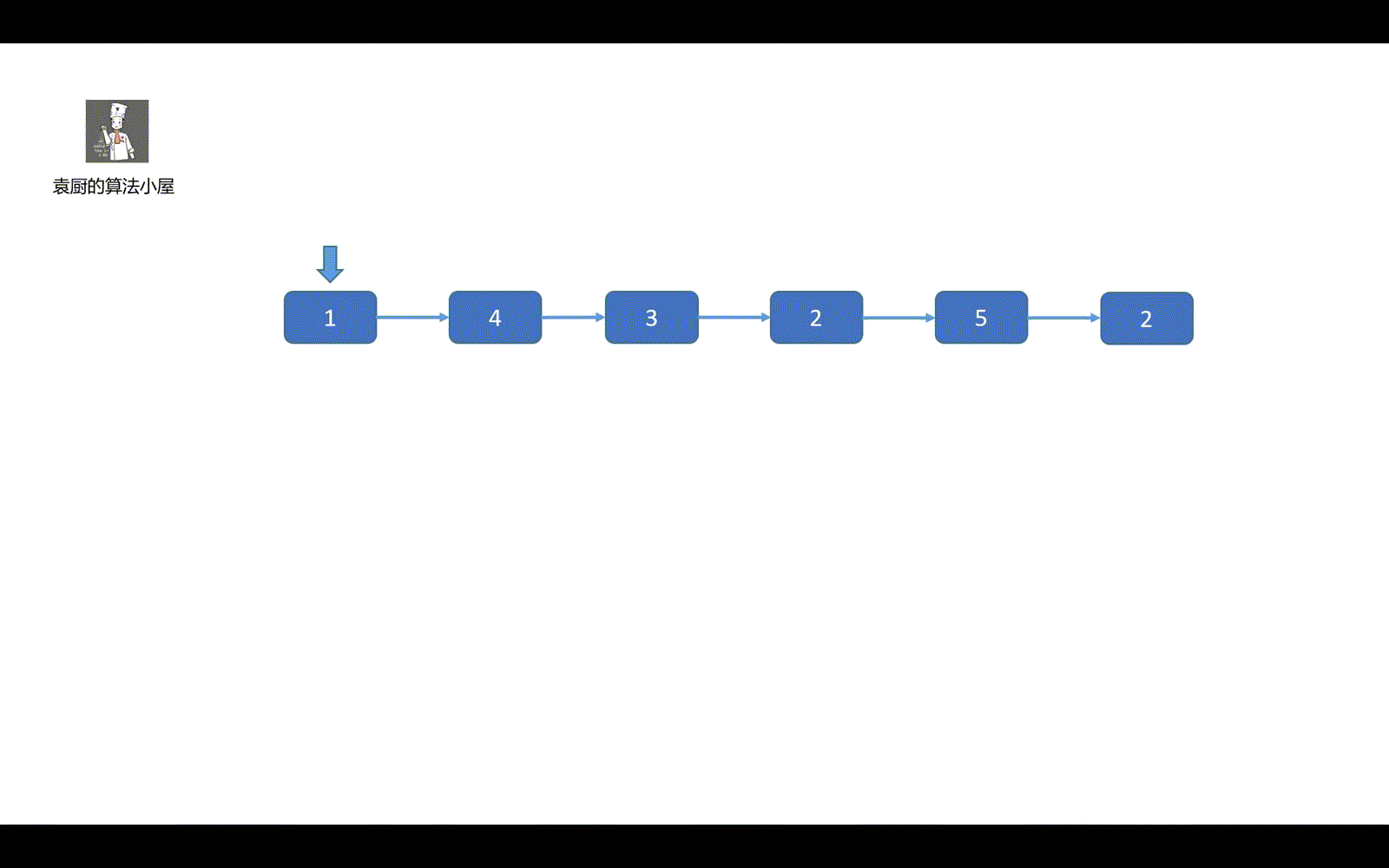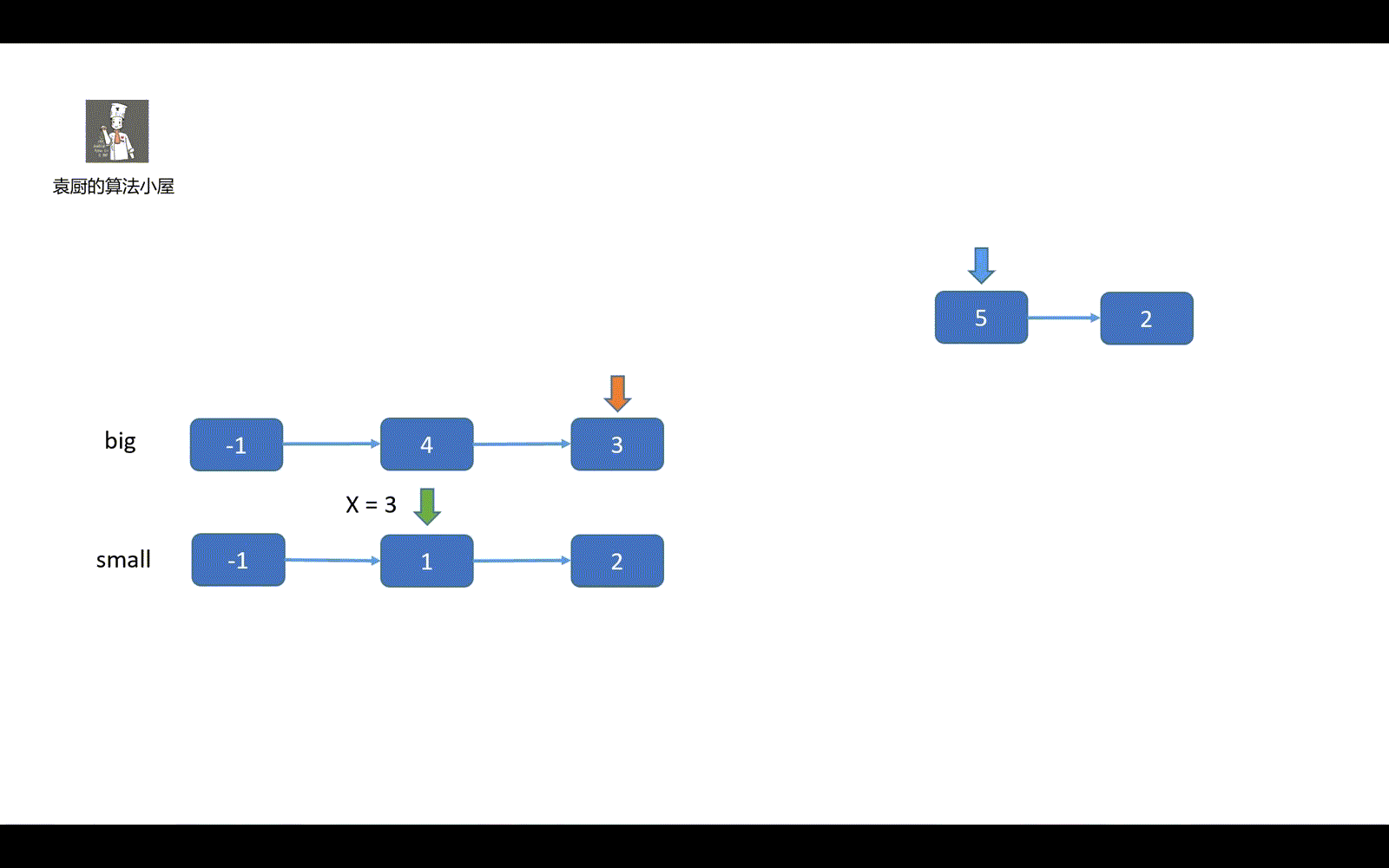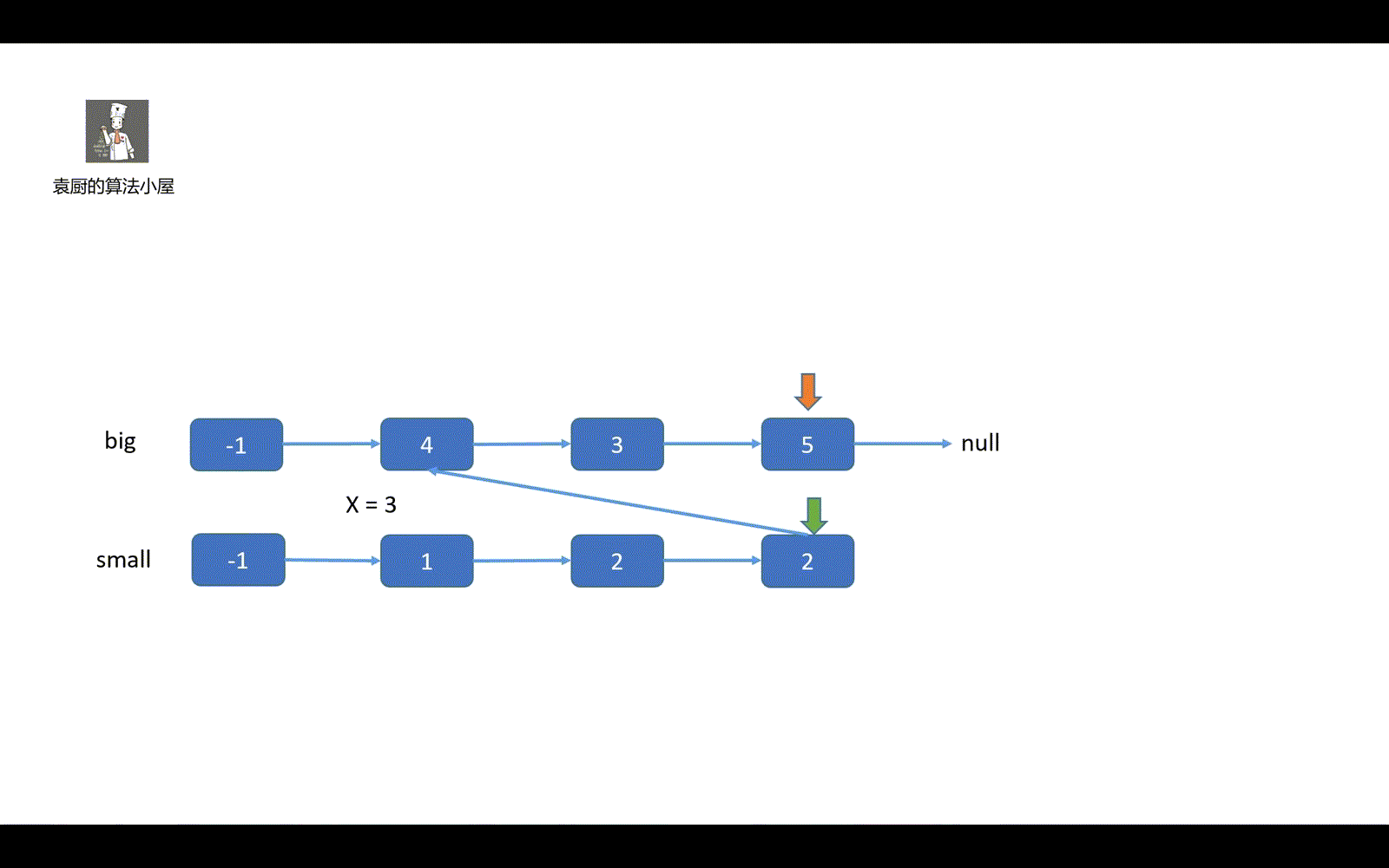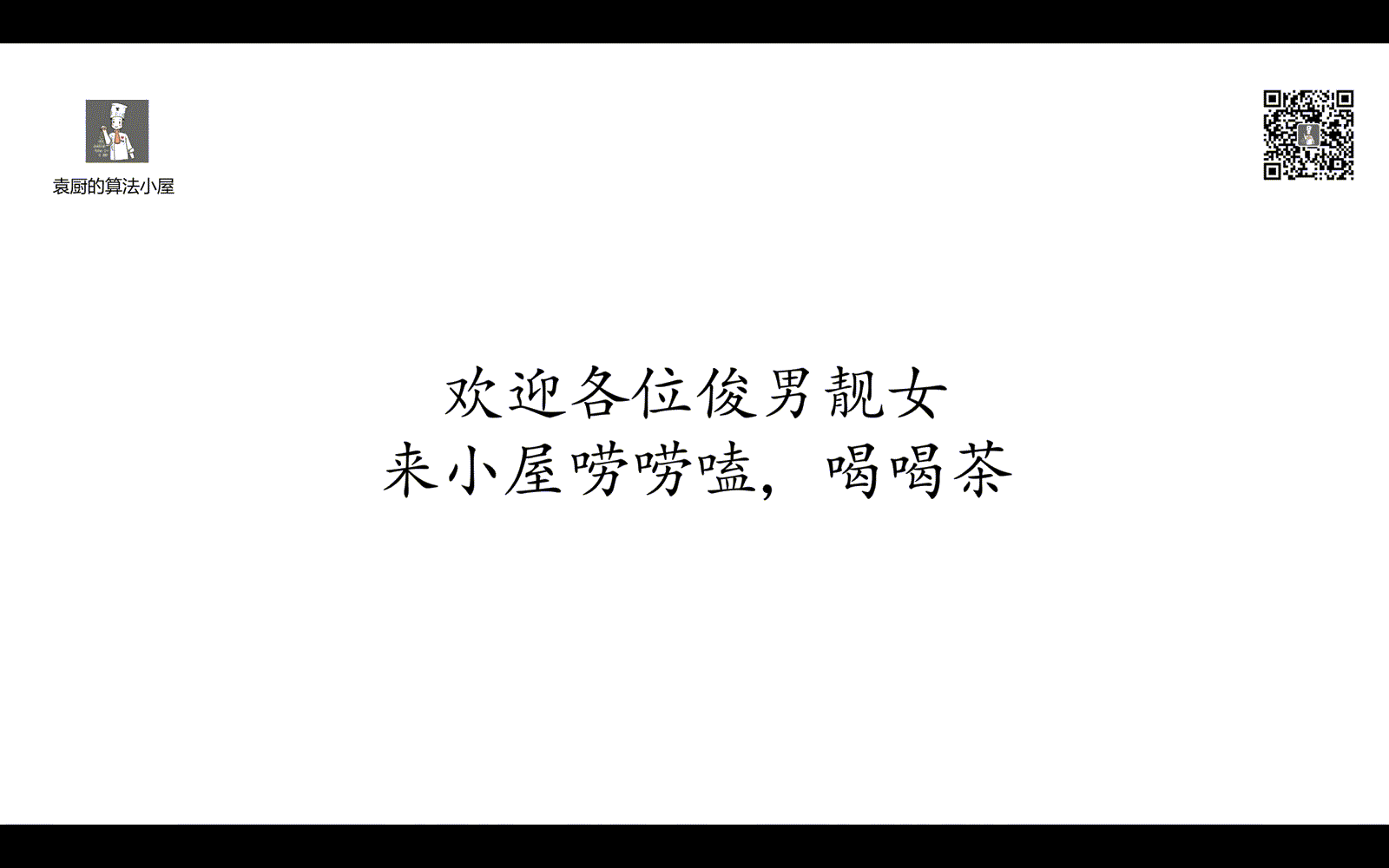
这个题目我的做题思路是这样的,我们先创建一个侦察兵,侦察兵负责比较链表值和 x 值,如果 >= 的话则接在 big 链表上,小于则接到 small 链表上,最后一个细节就是我们的 big 链表尾部要加上 null,不然会形成环。这是这个题目的一个小细节,很重要。
中心思想就是,将链表先分后合。
下面我们来看模拟视频吧。希望能给各位带来一丢丢帮助。
**题目代码**
Java Code:
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode pro = head;
ListNode big = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode small = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode headbig = big;
ListNode headsmall = small;
//分
while (pro != null) {
//大于时,放到 big 链表上
if (pro.val >= x) {
big.next = pro;
big = big.next;
//小于时,放到 small 链表上
}else {
small.next = pro;
small = small.next;
}
pro = pro.next;
}
//细节
big.next = null;
//合
small.next = headbig.next;
return headsmall.next;
}
}
```
C++ Code:
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
ListNode * pro = head;
ListNode * big = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode * small = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode * headbig = big;
ListNode * headsmall = small;
//分
while (pro != nullptr) {
//大于时,放到 big 链表上
if (pro->val >= x) {
big->next = pro;
big = big->next;
//小于时,放到 small 链表上
}else {
small->next = pro;
small = small->next;
}
pro = pro->next;
}
//细节
big->next = nullptr;
//合
small->next = headbig->next;
return headsmall->next;
}
};
```
JS Code:
```js
var partition = function(head, x) {
let pro = head;
let big = new ListNode(-1);
let small = new ListNode(-1);
let headbig = big;
let headsmall = small;
//分
while (pro) {
//大于时,放到 big 链表上
if (pro.val >= x) {
big.next = pro;
big = big.next;
//小于时,放到 small 链表上
}else {
small.next = pro;
small = small.next;
}
pro = pro.next;
}
//细节
big.next = null;
//合
small.next = headbig.next;
return headsmall.next;
};
```
Python Code:
```python
class Solution:
def partition(self, head: ListNode, x: int) -> ListNode:
pro = head
big = ListNode(-1)
small = ListNode(-1)
headbig = big
headsmall = small
# 分
while pro is not None:
# 大于时,放到 big 链表上
if pro.val >= x:
big.next = pro
big = big.next
# 小于时,放到 small 链表上
else:
small.next = pro
small = small.next
pro = pro.next
# 细节
big.next = None
# 合
small.next = headbig.next
return headsmall.next
```
Swift Code:
```swift
class Solution {
func partition(_ head: ListNode?, _ x: Int) -> ListNode? {
var pro = head
var big = ListNode(-1)
var small = ListNode(-1)
var headbig = big
var headsmall = small
//分
while pro != nil {
//大于时,放到 big 链表上
if pro!.val >= x {
big.next = pro
big = big.next!
//小于时,放到 small 链表上
} else {
small.next = pro
small = small.next!
}
pro = pro?.next
}
//细节
big.next = nil
//合
small.next = headbig.next
return headsmall.next
}
}
```