mirror of
https://github.com/chefyuan/algorithm-base.git
synced 2024-11-24 13:03:41 +00:00
144 lines
3.9 KiB
Markdown
144 lines
3.9 KiB
Markdown
> 如果阅读时,发现错误,或者动画不可以显示的问题可以添加我微信好友 **[tan45du_one](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/tan45du.github.io/master/个人微信.15egrcgqd94w.jpg)** ,备注 github + 题目 + 问题 向我反馈
|
||
>
|
||
> 感谢支持,该仓库会一直维护,希望对各位有一丢丢帮助。
|
||
>
|
||
> 另外希望手机阅读的同学可以来我的 <u>[**公众号:程序厨**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png)</u> 两个平台同步,想要和题友一起刷题,互相监督的同学,可以在我的小屋点击<u>[**刷题小队**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tan45du/test/master/微信图片_20210320152235.2pthdebvh1c0.png)</u>进入。
|
||
|
||
### [141. 环形链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/)
|
||
|
||
下面我们再来了解一种双指针,我们称之为快慢指针,顾名思义一个指针速度快,一个指针速度慢。
|
||
|
||
#### 题目描述
|
||
|
||
> 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。pos 代表环的入口,若为-1,则代表无环。
|
||
>
|
||
> 如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。否则,返回 false 。
|
||
|
||
示例 1:
|
||
|
||
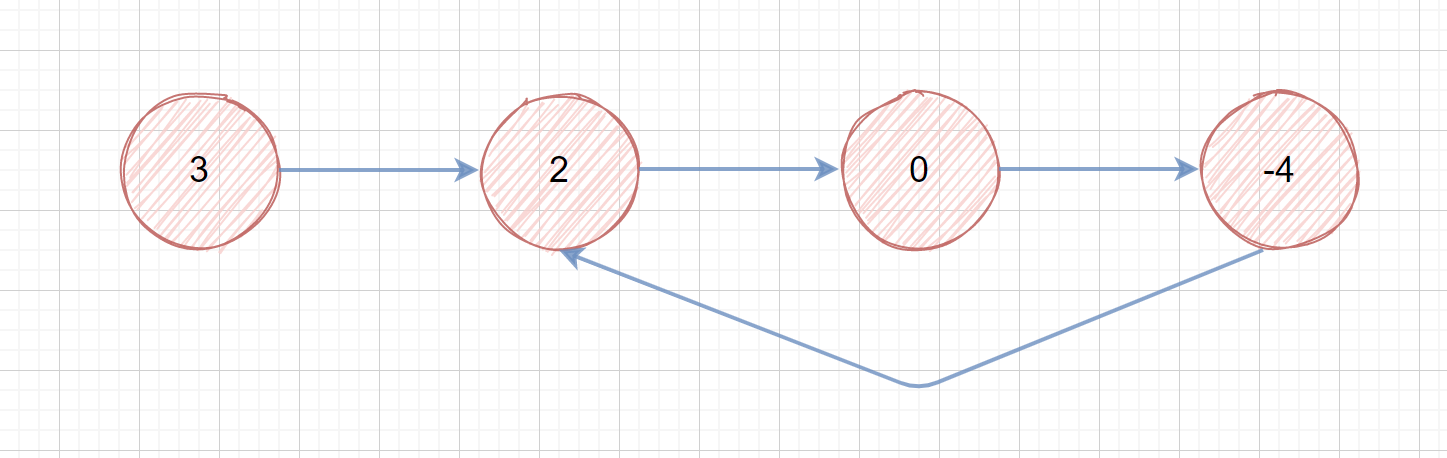
|
||
|
||
> 输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
|
||
> 输出:true
|
||
> 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
|
||
|
||
#### 题目解析
|
||
|
||
题目很容易理解,让我们判断链表中是否有环,我们只需通过我们的快慢指针即可,我们试想一下,如果链表中有环的话,一个速度快的指针和一个速度慢的指针在环中运动的话,若干圈后快指针肯定可以追上慢指针的。这是一定的。
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
好啦,做题思路已经有了,让我们一起看一下代码的执行过程吧。
|
||
|
||
**动画模拟**
|
||
|
||
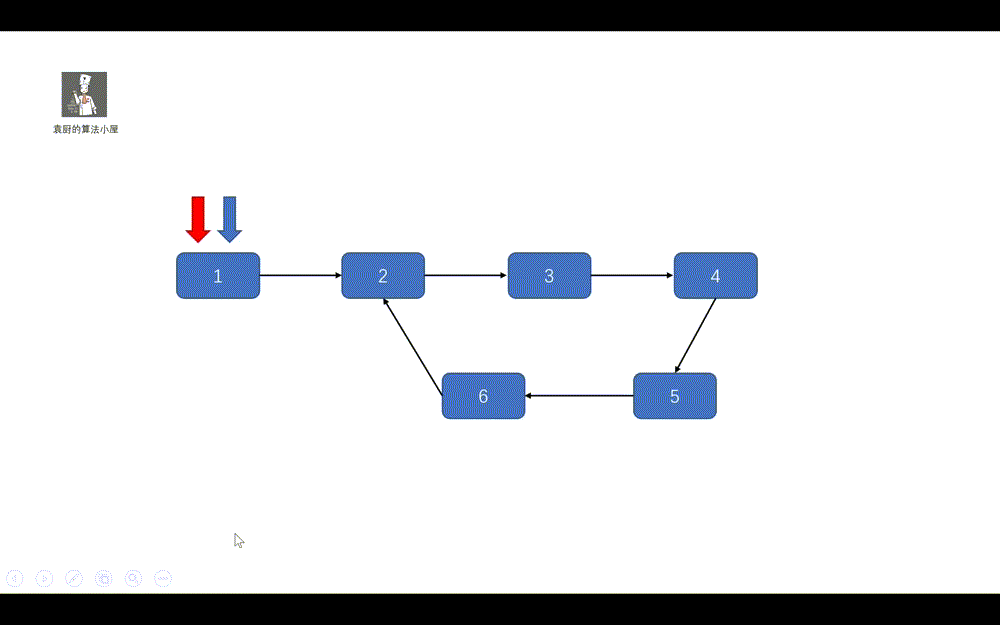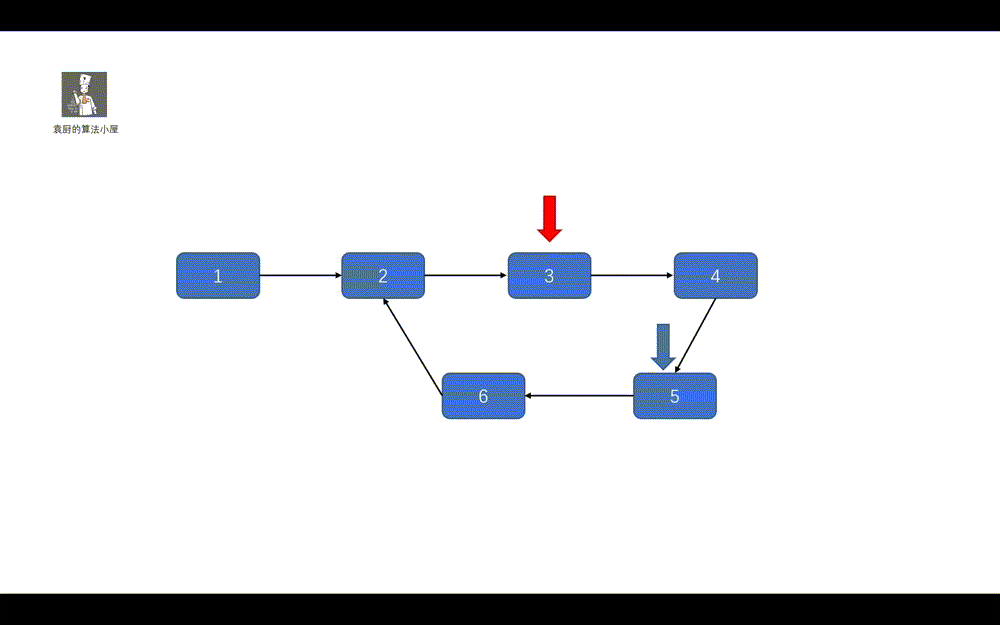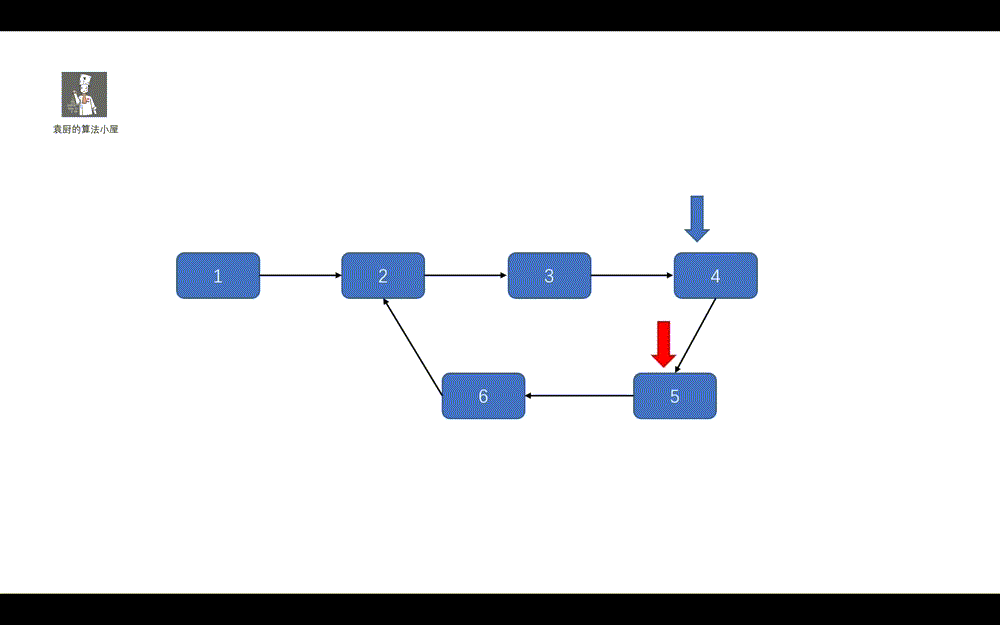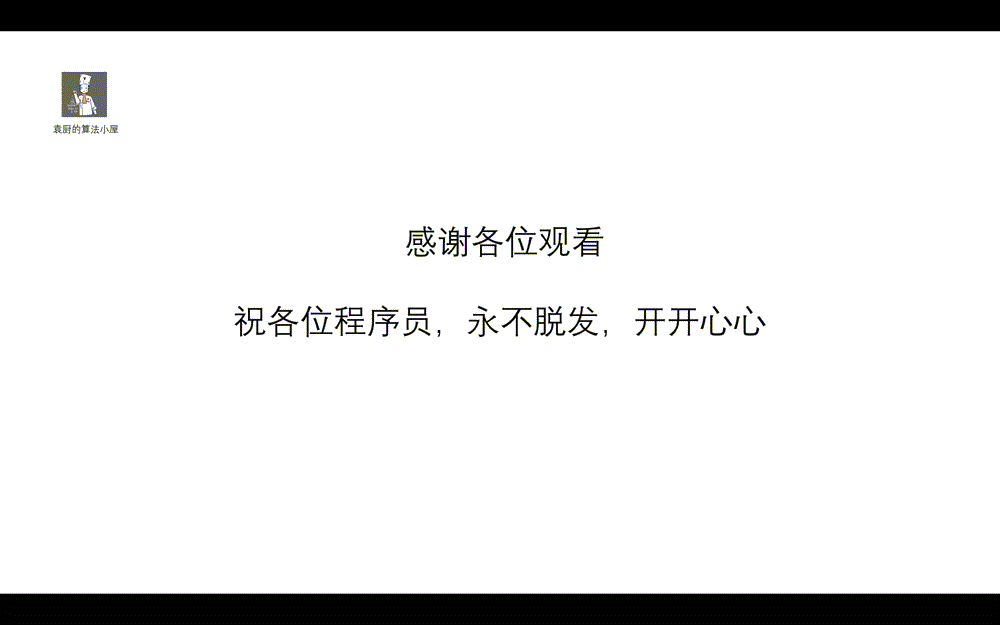
|
||
|
||
**题目代码**
|
||
|
||
Java Code:
|
||
|
||
```java
|
||
public class Solution {
|
||
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
|
||
ListNode fast = head;
|
||
ListNode low = head;
|
||
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
|
||
fast = fast.next.next;
|
||
low = low.next;
|
||
if (fast == low) {
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
C++ Code:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
|
||
ListNode * fast = head;
|
||
ListNode * slow = head;
|
||
while (fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) {
|
||
fast = fast->next->next;
|
||
slow = slow->next;
|
||
if (fast == slow) {
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
JS Code:
|
||
|
||
```javascript
|
||
var hasCycle = function (head) {
|
||
let fast = head;
|
||
let slow = head;
|
||
while (fast && fast.next) {
|
||
fast = fast.next.next;
|
||
slow = slow.next;
|
||
if (fast === slow) {
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Python Code:
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
|
||
fast = head
|
||
slow = head
|
||
while fast and fast.next:
|
||
fast = fast.next.next
|
||
slow = slow.next
|
||
if fast == slow:
|
||
return True
|
||
return False
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Swift Code:
|
||
|
||
```swift
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
func hasCycle(_ head: ListNode?) -> Bool {
|
||
var fast = head, slow = head
|
||
while fast != nil && fast?.next != nil {
|
||
fast = fast?.next?.next
|
||
slow = slow?.next
|
||
if fast === slow {
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Go Code:
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
func hasCycle(head *ListNode) bool {
|
||
if head == nil { return false }
|
||
s, f := head, head
|
||
for f != nil && f.Next != nil {
|
||
s = s.Next
|
||
f = f.Next.Next
|
||
if s == f {
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
```
|