10 KiB
如果阅读时,发现错误,或者动画不可以显示的问题可以添加我微信好友 tan45du_one ,备注 github + 题目 + 问题 向我反馈
感谢支持,该仓库会一直维护,希望对各位有一丢丢帮助。
另外希望手机阅读的同学可以来我的 公众号:袁厨的算法小屋 两个平台同步,想要和题友一起刷题,互相监督的同学,可以在我的小屋点击刷题小队进入。
1438. 绝对差不超过限制的最长连续子数组
给你一个整数数组 nums ,和一个表示限制的整数 limit,请你返回最长连续子数组的长度,该子数组中的任意两个元素之间的绝对差必须小于或者等于 limit 。
如果不存在满足条件的子数组,则返回 0 。
示例
输入:nums = [10,1,2,4,7,2], limit = 5 输出:4 解释:满足题意的最长子数组是 [2,4,7,2],其最大绝对差 |2-7| = 5 <= 5 。
提示:
-
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5
-
1 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
-
0 <= limit <= 10^9
题目解析
我们结合题目,示例,提示来看,这个题目也可以使用滑动窗口的思想来解决。我们需要判断某个子数组是否满足最大绝对差不超过限制值。
那么我们应该怎么解决呢?
我们想一下,窗口内的最大绝对差,如果我们知道窗口的最大值和最小值,最大值减去最小值就能得到最大绝对差。
所以我们这个问题就变成了获取滑动窗口内的最大值和最小值问题,哦?滑动窗口的最大值,是不是很熟悉,大家可以先看一下滑动窗口的最大值这个题目,那我们完全可以借助刚才题目的思想来解决这个题目。啪的一下我就搞懂了。
滑动窗口的最大值,我们当时借助了双端队列,来维护一个单调递减的双端队列,进而得到滑动窗口的最大值
那么我们同样可以借助双端队列,来维护一个单调递增的双端队列,来获取滑动窗口的最小值。既然知道了最大值和最小值,我们就可以判断当前窗口是否符合要求,如果符合要求则扩大窗口,不符合要求则缩小窗口,循环结束返回最大的窗口值即可。
下面我们来看一下我们的动画模拟,一下就能看懂!
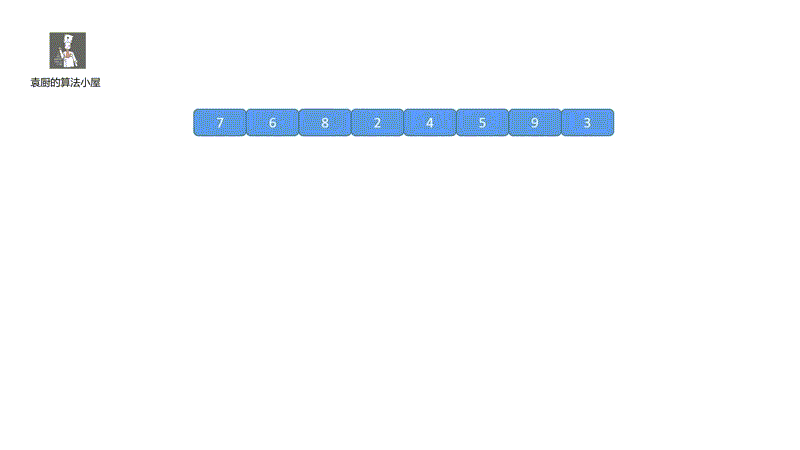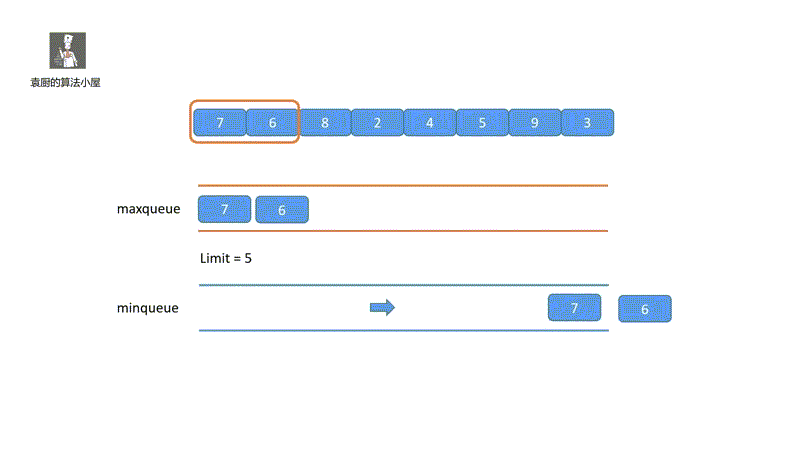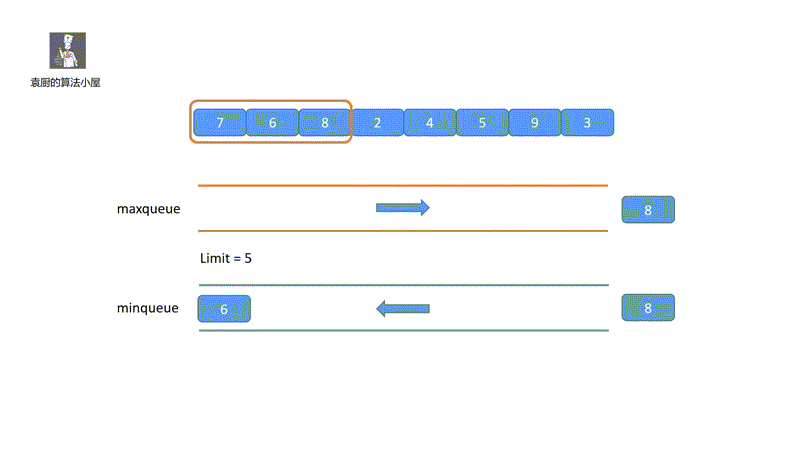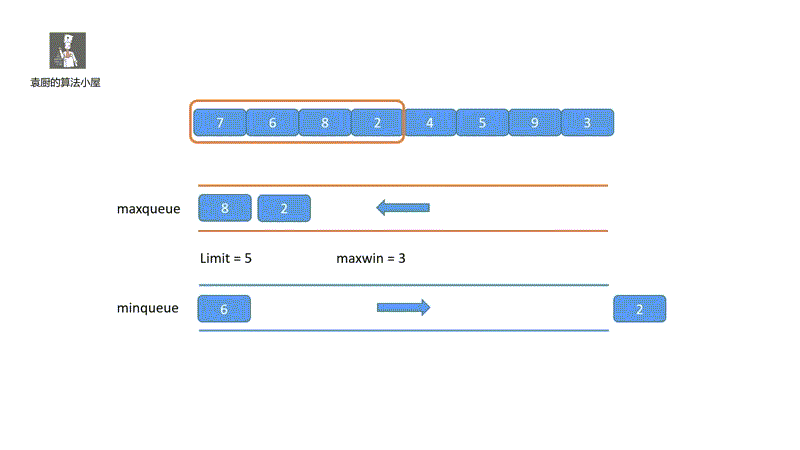
其实,我们只要把握两个重点即可,我们的 maxdeque 维护的是一个单调递减的双端队列,头部为当前窗口的最大值, mindeque 维护的是一个单调递增的双端队列,头部为窗口的最小值,即可。好啦我们一起看代码吧。
Java Code:
class Solution {
public int longestSubarray(int[] nums, int limit) {
Deque<Integer> maxdeque = new LinkedList<>();
Deque<Integer> mindeque = new LinkedList<>();
int len = nums.length;
int right = 0, left = 0, maxwin = 0;
while (right < len) {
while (!maxdeque.isEmpty() && maxdeque.peekLast() < nums[right]) {
maxdeque.removeLast();
}
while (!mindeque.isEmpty() && mindeque.peekLast() > nums[right]) {
mindeque.removeLast();
}
//需要更多视频解算法,可以来我的公众号:袁厨的算法小屋
maxdeque.addLast(nums[right]);
mindeque.addLast(nums[right]);
while (maxdeque.peekFirst() - mindeque.peekFirst() > limit) {
if (maxdeque.peekFirst() == nums[left]) maxdeque.removeFirst();
if (mindeque.peekFirst() == nums[left]) mindeque.removeFirst();
left++;
}
//保留最大窗口
maxwin = Math.max(maxwin,right-left+1);
right++;
}
return maxwin;
}
}
Python Code:
from typing import List
import collections
class Solution:
def longestSubarray(self, nums: List[int], limit: int)->int:
maxdeque = collections.deque()
mindeque = collections.deque()
leng = len(nums)
right = 0
left = 0
maxwin = 0
while right < leng:
while len(maxdeque) != 0 and maxdeque[-1] < nums[right]:
maxdeque.pop()
while len(mindeque) != 0 and mindeque[-1] > nums[right]:
mindeque.pop()
maxdeque.append(nums[right])
mindeque.append(nums[right])
while (maxdeque[0] - mindeque[0]) > limit:
if maxdeque[0] == nums[left]:
maxdeque.popleft()
if mindeque[0] == nums[left]:
mindeque.popleft()
left += 1
# 保留最大窗口
maxwin = max(maxwin, right - left + 1)
right += 1
return maxwin
Swift Code
Swift:数组模拟,超时(58 / 61 个通过测试用例)
class Solution {
func longestSubarray(_ nums: [Int], _ limit: Int) -> Int {
var maxQueue:[Int] = []
var minQueue:[Int] = []
let len = nums.count
var right = 0, left = 0, maxWin = 0
while right < len {
while !maxQueue.isEmpty && (maxQueue.last! < nums[right]) {
maxQueue.removeLast()
}
while !minQueue.isEmpty && (minQueue.last! > nums[right]) {
minQueue.removeLast()
}
maxQueue.append(nums[right])
minQueue.append(nums[right])
while (maxQueue.first! - minQueue.first!) > limit {
if maxQueue.first! == nums[left] {
maxQueue.removeFirst()
}
if minQueue.first! == nums[left] {
minQueue.removeFirst()
}
left += 1
}
maxWin = max(maxWin, right - left + 1)
right += 1
}
return maxWin
}
}
Swift:使用双端队列(击败了 100.00%)
class Solution {
func longestSubarray(_ nums: [Int], _ limit: Int) -> Int {
var maxQueue = Deque<Int>.init()
var minQueue = Deque<Int>.init()
let len = nums.count
var right = 0, left = 0, maxWin = 0
while right < len {
while !maxQueue.isEmpty && (maxQueue.peekBack()! < nums[right]) {
maxQueue.dequeueBack()
}
while !minQueue.isEmpty && (minQueue.peekBack()! > nums[right]) {
minQueue.dequeueBack()
}
maxQueue.enqueue(nums[right])
minQueue.enqueue(nums[right])
while (maxQueue.peekFront()! - minQueue.peekFront()!) > limit {
if maxQueue.peekFront()! == nums[left] {
maxQueue.dequeue()
}
if minQueue.peekFront()! == nums[left] {
minQueue.dequeue()
}
left += 1
}
maxWin = max(maxWin, right - left + 1)
right += 1
}
return maxWin
}
// 双端队列数据结构
public struct Deque<T> {
private var array: [T?]
private var head: Int
private var capacity: Int
private let originalCapacity: Int
public init(_ capacity: Int = 10) {
self.capacity = max(capacity, 1)
originalCapacity = self.capacity
array = [T?](repeating: nil, count: capacity)
head = capacity
}
public var isEmpty: Bool {
return count == 0
}
public var count: Int {
return array.count - head
}
public mutating func enqueue(_ element: T) {
array.append(element)
}
public mutating func enqueueFront(_ element: T) {
if head == 0 {
capacity *= 2
let emptySpace = [T?](repeating: nil, count: capacity)
array.insert(contentsOf: emptySpace, at: 0)
head = capacity
}
head -= 1
array[head] = element
}
public mutating func dequeue() -> T? {
guard head < array.count, let element = array[head] else { return nil }
array[head] = nil
head += 1
if capacity >= originalCapacity && head >= capacity*2 {
let amountToRemove = capacity + capacity/2
array.removeFirst(amountToRemove)
head -= amountToRemove
capacity /= 2
}
return element
}
public mutating func dequeueBack() -> T? {
if isEmpty {
return nil
} else {
return array.removeLast()
}
}
public func peekFront() -> T? {
if isEmpty {
return nil
} else {
return array[head]
}
}
public func peekBack() -> T? {
if isEmpty {
return nil
} else {
return array.last!
}
}
}
}
Go Code:
func longestSubarray(nums []int, limit int) int {
maxdeq := []int{} // 递减队列
mindeq := []int{} // 递增队列
length := len(nums)
left, right, maxwin := 0, 0, 0
for right < length {
for len(maxdeq) != 0 && maxdeq[len(maxdeq) - 1] < nums[right] {
maxdeq = maxdeq[: len(maxdeq) - 1]
}
maxdeq = append(maxdeq, nums[right])
for len(mindeq) != 0 && mindeq[len(mindeq) - 1] > nums[right] {
mindeq = mindeq[: len(mindeq) - 1]
}
mindeq = append(mindeq, nums[right])
for maxdeq[0] - mindeq[0] > limit {
if maxdeq[0] == nums[left] {
maxdeq = maxdeq[1:]
}
if mindeq[0] == nums[left] {
mindeq = mindeq[1:]
}
left++
}
maxwin = max(maxwin, right - left + 1)
right++
}
return maxwin
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}