24 lines
3.1 KiB
Go
24 lines
3.1 KiB
Go
## What is Docker
|
|
|
|
Docker is an in-company project launched by Solomon Hykes who is the founder of dotCloud when he was in France, it's a revolution based on dotCloud's years of cloud service experience, and [open-sourced with Apache 2.0 in 2013.03][docker-soft] maintained in [GitHub](https://github.com/moby/moby). Then, Docker joined the Linux Foundation and promoted [Open Containers Initlative (OCI)](https://www.opencontainers.org/).
|
|
|
|
Docker has aroused widespread concerns and discussions and had 52K stars and 10K forks in its [GitHub page](https://github.com/moby/moby) since being open-sourced. At the end of 2013, [dotCloud even decided to rename it to Docker](https://blog.docker.com/2013/10/dotcloud-is-becoming-docker-inc/) due to the popularity of the project. Docker was developed in Ubuntu 12.04 at the beginning. Red Hat has supported Dokcer since RHEL 6.5. Google has also widely applied Docker in its PaaS products.
|
|
|
|
Docker is developed with [GO](https://golang.org/) launched by Google, based on [cgroup](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cgroups) and [namespace](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linux_namespaces) of Linux Kernel and [Union FS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Union_mount) like [AUFS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aufs) to package and isolate the processes which belong to [Operating system level virtualization technology](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operating-system-level_virtualization). It is also called container because of the fact that the isolated processes are independent of the host and other isolated processes. The initial implementation is based on [LXC](https://linuxcontainers.org/lxc/introduction/). It removed LXC and use [libcontainer](https://github.com/docker/libcontainer) instead which is developed by themself since 0.7. Starting with 1.11, it uses [runC](https://github.com/opencontainers/runc) and [containerd](https://github.com/containerd/containerd) further.
|
|
|
|
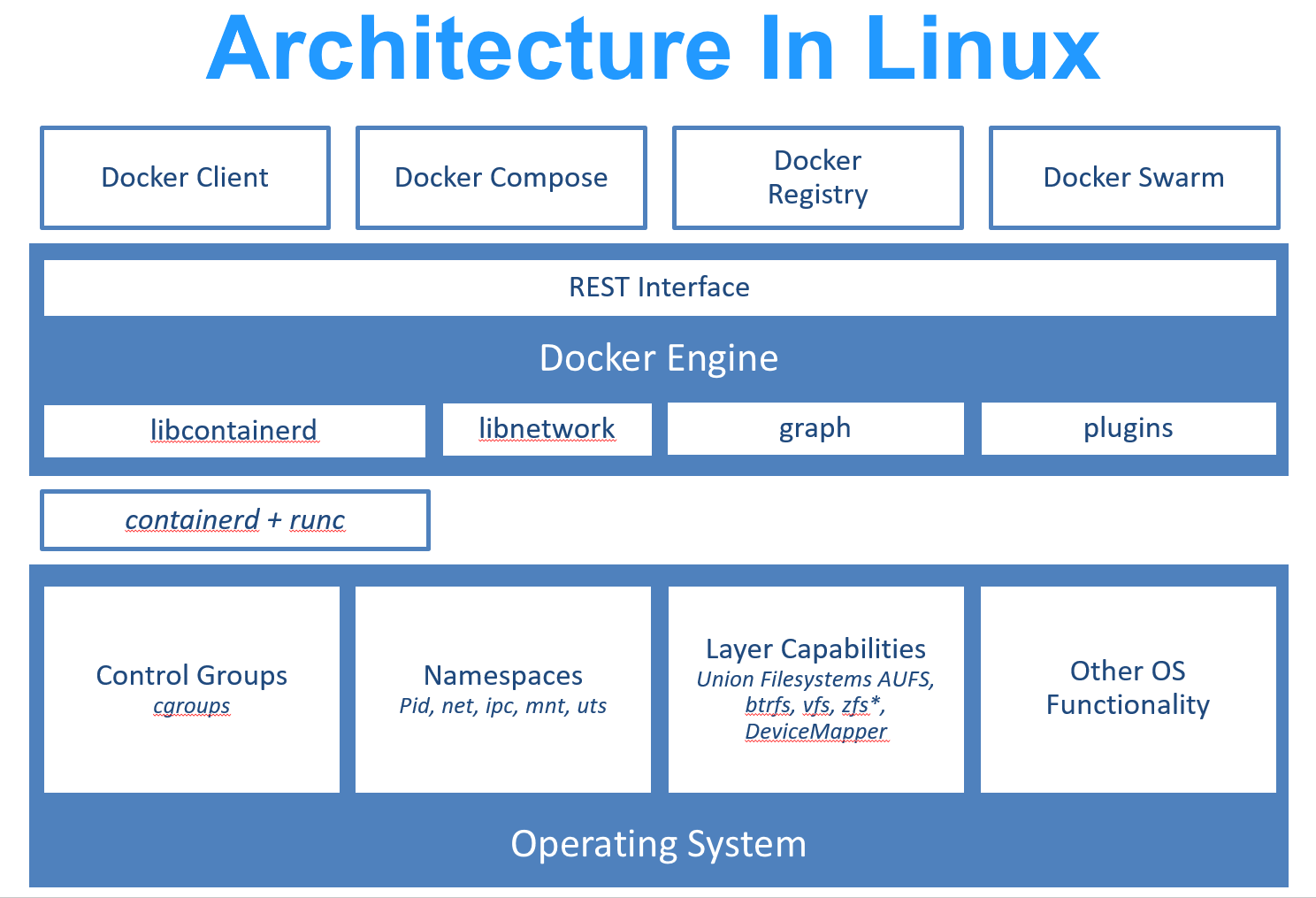
|
|
|
|
> `runc` is a Linux command-line tool for creating and running containers according to the [OCI container runtime specification](https://github.com/opencontainers/runtime-spec).
|
|
|
|
> `containerd` is a daemon that manages container life cycle from downloading and unpacking the container image to container execution and supervision.
|
|
|
|
Docker is further packaged on a container basis, from file system, network interconnection to process isolation, etc, greatly simplifying container craetion and maintenance.
|
|
|
|
The images below compare the differences between Docker and Traditional Virtualization. The traditional Virtual Machine technology is to virtualize a set of hardwares to run a complete operation system and run the required application process on this system. The application process in the container runs directly on the host kernel, and the container does not have its own Kernel and hardware virtualiztion. Therefore, containers are lighter than traditional virtual machines.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
[docker-soft]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Docker_(software)
|